| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
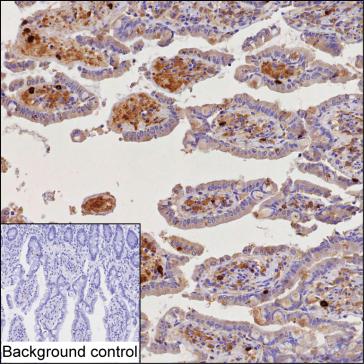
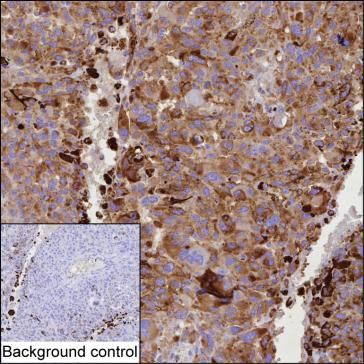
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD63 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是与CD63抗体相关的3-4篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids*
**作者**:Théry, C., Amigorena, S., Raposo, G., & Clayton, A.
**摘要**:该文献详细描述了外泌体分离和鉴定的标准化方法,其中CD63被广泛用作外泌体特异性标记物。作者通过Western blot和流式细胞术验证了CD63抗体在外泌体检测中的有效性,强调其在区分外泌体与其他细胞囊泡中的重要性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*CD63 regulates Epstein-Barr virus LMP1-mediated NF-κB signaling and cell survival*
**作者**:Keryer-Bibens, C., Pioche-Durieu, C., Villemant, C., et al.
**摘要**:本文探讨了CD63在EB病毒潜伏膜蛋白1(LMP1)信号传导中的作用,发现CD63抗体可阻断LMP1与细胞膜微区的结合,抑制NF-κB通路的激活,从而影响肿瘤细胞存活。研究为CD63在病毒相关癌症中的治疗潜力提供了依据。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Tetraspanin CD63 promotes vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-β1 integrin complex formation, thereby regulating activation and downstream signaling in endothelial cells*
**作者**:Sung, B.H., Ketova, T., Hoshino, D., et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了CD63通过促进VEGFR2与β1整合素的相互作用调控血管生成。利用CD63抗体进行功能阻断实验,证实其可抑制内皮细胞迁移和血管生成信号通路,为抗血管生成治疗提供了新靶点。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based assays for exosome biomarker development*
**作者**:Van Deun, J., Mestdagh, P., & Vandesompele, J.
**摘要**:本文评估了多种外泌体标记物抗体的特异性,包括CD63.研究发现不同来源的CD63抗体在灵敏度和交叉反应性上存在差异,强调了抗体标准化在临床诊断中的必要性。
---
以上文献覆盖了CD63在外泌体研究、信号通路调控及抗体应用中的关键作用,可作为相关实验设计的参考。
CD63 antibody targets the CD63 antigen, a member of the tetraspanin transmembrane protein family. CD63 is widely expressed in various cell types, primarily localized in lysosomal and endosomal membranes, but also present on the cell surface and enriched in extracellular vesicles like exosomes. It plays roles in cell signaling, adhesion, and migration by interacting with integrins, receptors, and other tetraspanins.
CD63 is a key marker for exosome identification, making its antibody a critical tool in extracellular vesicle research. In disease contexts, CD63 has been implicated in cancer progression, immune regulation, and neurodegenerative disorders. For example, elevated CD63 levels correlate with tumor metastasis and poor prognosis, while its dysregulation is linked to impaired lysosomal function in diseases like Alzheimer's.
Antibodies against CD63 are widely used in techniques such as flow cytometry, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence to study exosome biogenesis, vesicle trafficking, and cellular interactions. They also hold diagnostic potential for liquid biopsies and therapeutic targeting. However, variability in antibody specificity across isoforms or post-translational modifications requires careful validation for experimental accuracy. Research continues to explore CD63's role as a biomarker or therapeutic target in precision medicine.
×