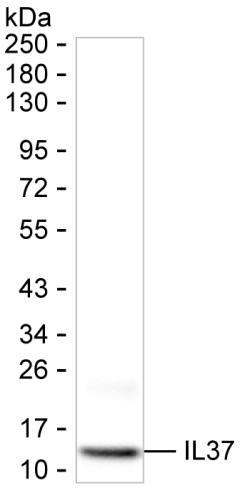
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human IL37 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于IL-37抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Interleukin-37: a new cytokine with anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects*
**作者**:Charles A. Dinarello et al.
**摘要**:该综述总结了IL-37作为抗炎细胞因子的生物学功能,提出其通过抑制NF-κB和MAPK信号通路减轻炎症反应。研究还探讨了使用IL-37中和抗体在动物模型中验证其调控炎症性肠病(IBD)的作用机制。
2. **文献名称**:*Therapeutic potential of anti-IL-37 antibodies in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis*
**作者**:Li J. et al.
**摘要**:研究发现,在多发性硬化症(MS)的小鼠模型中,阻断IL-37的单克隆抗体可增强Th17细胞的活性,加剧神经炎症反应,提示IL-37在自身免疫疾病中的保护性作用,并为靶向IL-37的抗体治疗提供理论依据。
3. **文献名称**:*IL-37 inhibits pyroptosis by targeting caspase-1 via IL-1R8 in inflammatory diseases*
**作者**:Nold-Petry C.A. et al.
**摘要**:通过体外和体内实验证明,IL-37通过结合IL-1R8受体抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化。研究利用IL-37特异性抗体揭示其在脓毒症和关节炎模型中抑制细胞焦亡(pyroptosis)的关键机制。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science核对最新研究。IL-37抗体的研究多聚焦于炎症、自身免疫病及感染领域,近年亦有临床转化探索。
Interleukin-37 (IL-37) is a cytokine belonging to the interleukin-1 (IL-1) family, first identified in 2000. Unlike most pro-inflammatory IL-1 members, IL-37 functions as a natural suppressor of innate immunity and inflammation, playing a critical role in maintaining immune homeostasis. It is produced by various immune and non-immune cells, including macrophages, epithelial cells, and T cells, often in response to inflammatory stimuli. IL-37 exerts its anti-inflammatory effects by binding to IL-18 receptor α (IL-18Rα) and interacting with SIGIRR (single immunoglobulin IL-1R-related molecule), which inhibits NF-κB and mTOR signaling pathways. This suppresses the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6.
Antibodies targeting IL-37 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. They enable detection via techniques such as ELISA, Western blot, and immunohistochemistry. Research using IL-37 antibodies has linked its dysregulation to autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus), chronic inflammation, and cancer, highlighting its therapeutic potential. Neutralizing antibodies are also explored to modulate IL-37 activity in diseases where excessive immunosuppression may be detrimental. However, challenges remain in standardizing antibody specificity and understanding IL-37’s pleiotropic roles across tissues. Ongoing studies aim to clarify its mechanisms and translational applications in immune-mediated disorders.
×