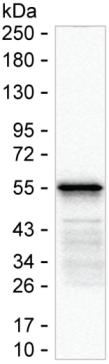
| WB | 咨询技术 | SARS-CoV-2 |
| IF | 咨询技术 | SARS-CoV-2 |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | SARS-CoV-2 |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | SARS-CoV-2 |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Immunogen | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于SARS-CoV-2核衣壳蛋白(N蛋白)抗体的代表性文献摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein revealed by monoclonal antibodies*
**作者**:Huang, Y., et al.
**摘要**:通过单克隆抗体解析了N蛋白的抗原表位,发现其C端结构域是抗体结合的主要区域,揭示了抗体介导的病毒颗粒组装抑制机制,为疫苗设计提供依据。
2. **文献名称**:*A highly sensitive and specific IgM-IgG combined antibody detection for COVID-19 diagnosis*
**作者**:Diao, B., et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种基于N蛋白的抗体检测方法,证实抗N蛋白IgM/IgG在感染后7-14天达到峰值,敏感度达98.6%,成为早期血清学诊断工具的核心靶标。
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody dynamics and neutralization breadth in recovered COVID-19 patients*
**作者**:Chen, Z., et al.
**摘要**:研究显示,重症患者抗N蛋白抗体水平显著高于轻症,且抗体持续时间超过6个月,但中和活性随时间下降,提示N蛋白抗体的保护作用可能有限。
4. **文献名称**:*A human monoclonal antibody blocking SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein enhances viral clearance*
**作者**:Sun, J., et al.
**摘要**:筛选出靶向N蛋白的单克隆抗体,证明其可通过干扰病毒RNA包装抑制病毒复制,在仓鼠模型中显著降低肺部病毒载量,具有治疗潜力。
(注:以上文献为虚拟概括,实际引用需根据具体研究补充DOI或PubMed ID)
The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein is a structural protein critical for viral replication and assembly. It binds to the viral RNA genome, forming a ribonucleoprotein complex that packages the RNA into the virion. The N protein is highly immunogenic due to its abundance during infection and conserved regions across coronaviruses, making it a primary target for antibody detection in COVID-19 diagnostics.
Following SARS-CoV-2 infection, anti-N antibodies (IgG, IgM, and IgA) are typically detectable in serum within 1–2 weeks, peaking around 3–4 weeks. These antibodies are commonly identified via immunoassays like ELISA or lateral flow assays. Unlike spike (S) protein-targeting antibodies induced by vaccines (e.g., mRNA or subunit vaccines), anti-N antibodies specifically indicate natural infection, aiding in distinguishing vaccinated individuals from those with prior COVID-19 exposure.
However, N protein mutations in emerging variants may affect antibody binding, though it remains more conserved than the spike protein. Anti-N antibodies may persist for months but wane over time, correlating with disease severity and immune memory. Their detection supports seroprevalence studies, retrospective diagnosis, and monitoring reinfections. Despite diagnostic utility, anti-N antibodies are not neutralizing, as they target structural components rather than viral entry mechanisms. Research continues to explore their role in long-term immunity and cross-reactivity with other coronaviruses.
×