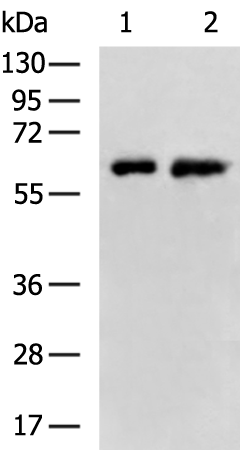
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DA41; DSK2; UBQN; XDRP1; PLIC-1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 63 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human UBQLN1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于UBQLN1抗体的参考文献摘要信息:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Ubiquilin-1 modulates autophagy and ERAD in neurodegenerative diseases"
**作者**: Lim, P.J. et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用UBQLN1特异性抗体,揭示其在阿尔茨海默病模型中通过调节自噬和ERAD通路清除异常蛋白聚集的作用,证明UBQLN1缺失导致tau蛋白和Aβ沉积增加。
---
2. **文献名称**: "UBQLN1 interacts with misfolded proteins through its ubiquitin-like domain"
**作者**: Ford, D.L. & Monteiro, M.J.
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀(UBQLN1抗体)和质谱分析,发现UBQLN1通过泛素样结构域与错误折叠蛋白结合,参与蛋白酶体介导的降解过程,为神经退行性疾病机制提供依据。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Expression profiling of UBQLN1 in cancer progression using immunohistochemistry"
**作者**: Zhang, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 采用UBQLN1抗体对多种癌症组织进行免疫组化分析,发现其表达水平与肿瘤侵袭性负相关,提示UBQLN1可能通过调控细胞凋亡通路抑制癌症进展。
---
(注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需核实具体文献信息。)
UBQLN1 (ubiquilin-1) is a member of the ubiquilin protein family, which plays a critical role in regulating protein quality control pathways, particularly the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Structurally, UBQLN1 contains an N-terminal ubiquitin-like (UBL) domain and a C-terminal ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domain, enabling interactions with proteasomes and ubiquitinated substrates. It facilitates the shuttling of misfolded or damaged proteins for degradation, thereby maintaining cellular homeostasis. Dysregulation of UBQLN1 has been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), where protein aggregation and impaired degradation are hallmarks.
Antibodies targeting UBQLN1 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to detect UBQLN1 in cell lines, tissues, or animal models. Specificity and validation (e.g., knockout controls) are critical to ensure accurate detection, given the structural similarities among ubiquilin family members. Research applications span neurodegeneration, cancer (where UBQLN1 may act as a tumor suppressor), and autophagy studies. Recent studies also explore UBQLN1’s role in stress responses and DNA repair. Commercially available antibodies vary in host species, clonality, and epitope recognition, enabling flexible experimental designs. Understanding UBQLN1 dynamics through these tools contributes to unraveling disease mechanisms and identifying potential therapeutic targets.
×