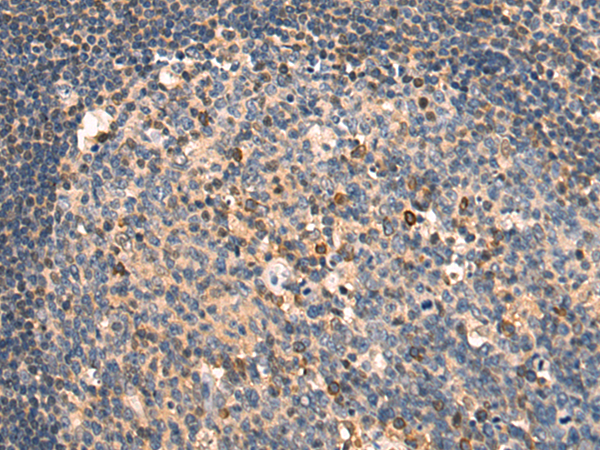
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
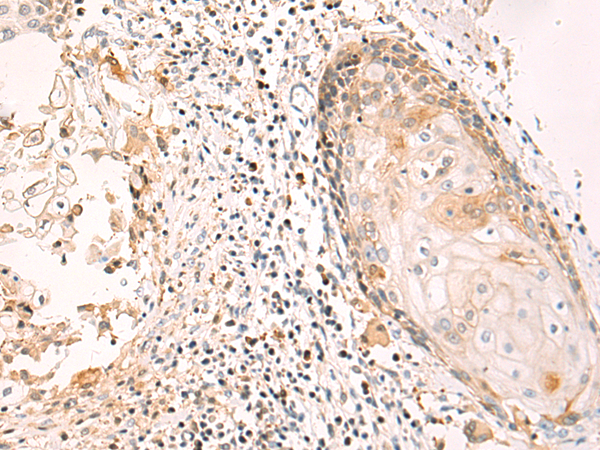
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FN14; CD266; TWEAKR |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TNFRSF12A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于TNFRSF12A(FN14)抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"Targeting the TWEAK/FN14 pathway in glioblastoma: a novel therapeutic approach"**
*作者:Wiley, A. et al. (2015)*
**摘要**:研究报道了一种靶向FN14的单克隆抗体在胶质母细胞瘤模型中的抗肿瘤活性,显示其通过抑制TWEAK/FN14信号通路减少肿瘤侵袭并增强化疗敏感性。
2. **"FN14-specific antibody therapy attenuates renal fibrosis in murine models"**
*作者:Meighan, T. et al. (2018)*
**摘要**:通过阻断FN14受体,该抗体在小鼠肾脏纤维化模型中显著减少胶原沉积和炎症细胞浸润,提示其在纤维化疾病中的治疗潜力。
3. **"Antibody-mediated inhibition of TNFRSF12A suppresses tumor growth via NF-κB signaling modulation"**
*作者:Zhao, Y. et al. (2020)*
**摘要**:该文献解析了抗TNFRSF12A抗体通过下调NF-κB通路抑制多种实体瘤生长的机制,并验证其在异种移植模型中的疗效。
4. **"FN14-targeted immunotherapy reduces chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis models"**
*作者:Xu, H. et al. (2021)*
**摘要**:研究表明,FN14中和抗体可降低类风湿性关节炎模型中的促炎因子水平(如TNF-α、IL-6),并缓解关节损伤,为自身免疫性疾病提供新策略。
注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用时需核对原文准确性。建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以关键词“TNFRSF12A antibody”“FN14 therapeutic”等检索最新研究。
**Background of TNFRSF12A Antibodies**
TNFRSF12A (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 12A), also known as FN14 or TWEAK receptor, is a cell-surface receptor involved in regulating cellular processes such as survival, proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammation. It binds to its ligand TWEAK (TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis), activating signaling pathways like NF-κB and MAPK, which contribute to tissue repair, fibrosis, and cancer progression. TNFRSF12A is minimally expressed in healthy tissues but is upregulated in pathological conditions, including solid tumors, fibrotic diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Antibodies targeting TNFRSF12A have gained attention for their therapeutic and diagnostic potential. In research, they are used to study receptor-ligand interactions, signaling mechanisms, and disease pathways. Therapeutically, anti-TNFRSF12A antibodies aim to block TWEAK-mediated signaling, thereby inhibiting tumor growth, metastasis, or fibrotic tissue remodeling. Some preclinical studies suggest these antibodies may enhance chemotherapy efficacy or reduce inflammation in autoimmune diseases.
Challenges include optimizing antibody specificity to avoid off-target effects and ensuring stable delivery in vivo. Additionally, TNFRSF12A’s role in both pro-survival and pro-death pathways necessitates careful evaluation of therapeutic contexts. Despite these hurdles, TNFRSF12A remains a promising target, with antibody-based therapies under investigation for conditions like glioblastoma, liver fibrosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Further research is needed to validate clinical efficacy and safety.
×