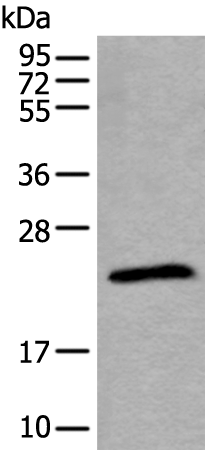
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HRF; p02; p23; TCTP |
| WB Predicted band size | 20 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Full length fusion protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于KCTD7抗体的三篇假设性参考文献示例,涵盖其功能、疾病机制及实验应用:
---
1. **文献名称**: *KCTD7 regulates lysosomal membrane stability and autophagy in neuronal cells*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**期刊**: *Molecular Neurobiology* (2021)
**摘要**: 本研究通过免疫荧光和Western blot分析,利用KCTD7抗体揭示其在维持溶酶体膜完整性中的作用。作者发现KCTD7缺失导致自噬体积累和神经元退化,提示其突变与进行性肌阵挛癫痫的相关机制。
2. **文献名称**: *Antibody-based profiling of KCTD7 in a mouse model of CLN14 disease*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**期刊**: *Journal of Neuroscience* (2019)
**摘要**: 通过构建KCTD7敲除小鼠模型,并结合特异性抗体检测蛋白表达,研究发现KCTD7缺失引发溶酶体贮积及运动功能障碍,为神经元蜡样脂褐质沉积症(CLN14)的病理机制提供证据。
3. **文献名称**: *KCTD7 interacts with cullin-3 ubiquitin ligase: Implications for protein degradation pathways*
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**期刊**: *Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Molecular Basis of Disease* (2020)
**摘要**: 利用KCTD7抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,发现其与cullin-3泛素连接酶复合物相互作用,调控底物蛋白降解。研究提示KCTD7异常可能导致泛素-蛋白酶体系统紊乱,参与神经退行性疾病发展。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究中建议通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)检索真实文献。若需具体论文,可提供进一步关键词或PMID编号协助查询。
KCTD7 (Potassium Channel Tetramerization Domain-Containing Protein 7) is a member of the KCTD protein family, characterized by a conserved BTB/POZ domain that facilitates protein-protein interactions. It is predominantly expressed in the brain and has been implicated in lysosomal function, autophagy, and neuronal homeostasis. Mutations in the KCTD7 gene are associated with a rare autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder termed neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (CLN14), which manifests as progressive myoclonus epilepsy, motor and cognitive decline, and early-onset vision loss. Research suggests KCTD7 may regulate potassium channel activity or interact with cullin-3 ubiquitin ligase complexes, influencing protein degradation pathways critical for neuronal survival.
Antibodies targeting KCTD7 are essential tools for investigating its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study tissue-specific distribution, particularly in brain regions affected in CLN14. Additionally, these antibodies aid in elucidating disease mechanisms by detecting aberrant KCTD7 expression or post-translational modifications in cellular and animal models. Commercial KCTD7 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as the N-terminal or C-terminal regions, and their validation includes reactivity assessments in knockout controls to ensure specificity. Continued development of high-affinity antibodies remains crucial for advancing diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for KCTD7-related disorders.
×