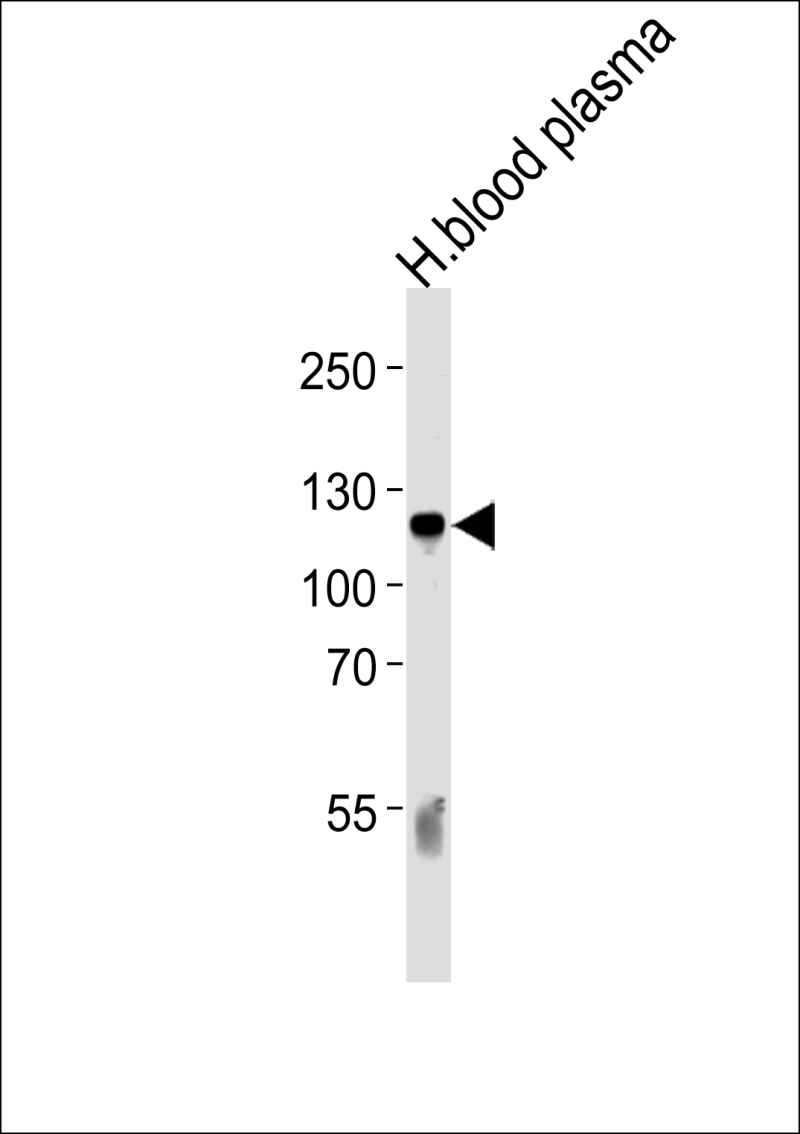
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
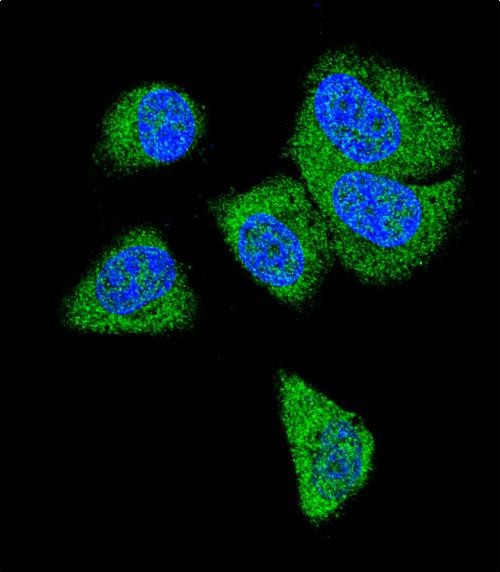
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
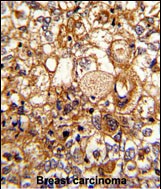
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
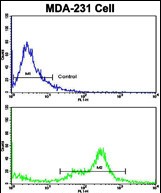
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Complement component C6, C6 |
| Entrez GeneID | 729 |
| WB Predicted band size | 104.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This C6 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 30-58 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human C6. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于TNF抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容概括整理:
1. **"Anti-TNF antibody therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of serious infections and malignancies"**
- **作者**: Keane J, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究分析了抗TNF抗体(如英夫利昔单抗)治疗类风湿性关节炎时,患者发生严重感染(如结核病)和恶性肿瘤的风险增加的现象,强调治疗前需进行感染筛查。
2. **"Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor α monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial"**
- **作者**: Maini RN, et al.
- **摘要**: 这项III期临床试验证明,英夫利昔单抗(抗TNF-α单抗)联合甲氨蝶呤可显著改善类风湿性关节炎患者的症状和影像学进展,确立了其在难治性疾病中的核心地位。
3. **"Adalimumab: a review of its use in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis"**
- **作者**: Scheinfeld N.
- **摘要**: 综述了阿达木单抗(全人源抗TNF单抗)的药理机制、临床试验数据及安全性,显示其单药或联合治疗可有效缓解症状并延缓关节损伤。
如果需要更具体的文献或补充,可进一步说明研究领域(如克罗恩病、副作用机制等)。
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antibodies are biologic agents designed to neutralize TNF, a pro-inflammatory cytokine central to immune regulation and inflammatory pathways. Discovered in the 1970s, TNF plays a dual role: it promotes host defense against infections but also drives chronic inflammation in autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and psoriasis. Dysregulated TNF signaling is linked to tissue damage and disease progression, prompting the development of TNF inhibitors as targeted therapies.
The first TNF antibody, infliximab, was approved in 1998 for Crohn’s disease and RA. It binds soluble and membrane-bound TNF, blocking interactions with its receptors (TNFR1/TNFR2) to suppress inflammation. Subsequent agents, including adalimumab (fully human monoclonal antibody) and certolizumab pegol (PEGylated Fab fragment), expanded treatment options. These drugs revolutionized management of autoimmune conditions, improving symptoms and slowing disease progression in many patients. However, TNF blockade carries risks, such as increased susceptibility to infections (e.g., tuberculosis) and potential drug-induced lupus, necessitating careful patient selection.
Ongoing research explores TNF’s complex biology, including its role in immune homeostasis and paradoxical effects in cancer. Next-generation therapies aim to enhance specificity or combine TNF inhibition with other targets to improve efficacy and safety profiles. TNF antibodies remain a cornerstone of immunomodulatory therapy, exemplifying the success of molecular-targeted drug development.
×