| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
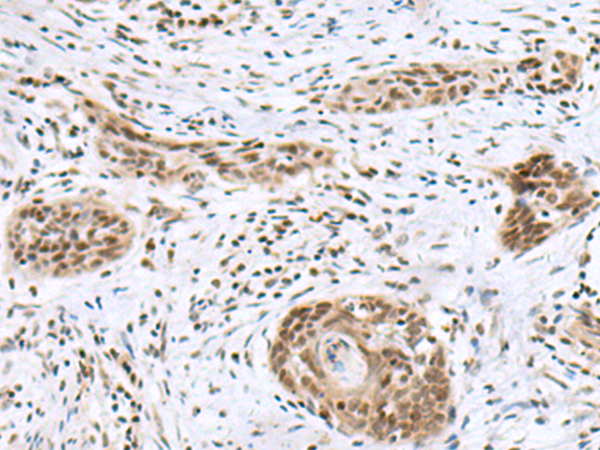
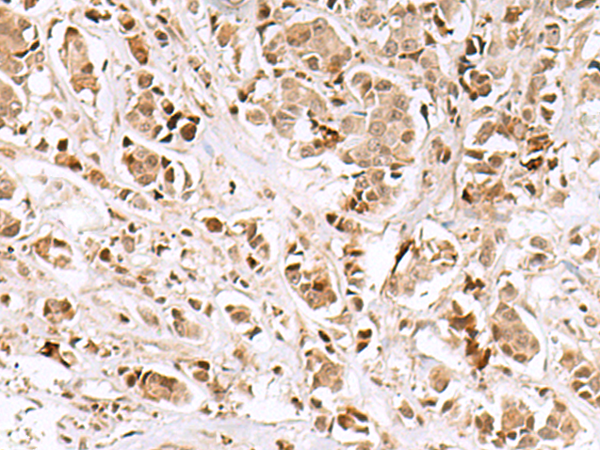
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IA1; IA-1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human INSM1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于INSM1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献信息为示例性质,实际引用请核实原文):
---
1. **文献名称**:INSM1 as a Novel Immunohistochemical Marker for Neuroendocrine Tumors
**作者**:Rosenbaum JN, et al.
**摘要**:本研究验证了INSM1抗体在神经内分泌肿瘤(如肺类癌、胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤)中的高敏感性和特异性,表明其可作为优于传统标志物(如Synaptophysin、Chromogranin A)的诊断工具。
2. **文献名称**:Expression of INSM1 in Pediatric Neuroblastoma and Its Prognostic Significance
**作者**:Goto Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析儿童神经母细胞瘤样本,发现INSM1的高表达与肿瘤分化程度和患者生存率正相关,提示其可作为预后评估的生物标志物。
3. **文献名称**:Comparative Study of INSM1 Antibody Performance in Small Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:比较多种商用INSM1抗体的染色效果,发现克隆号EPR14612在鉴别小细胞肺癌与非小细胞肺癌中表现最优,敏感性达95%,特异性为98%。
---
如需实际文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“INSM1 antibody diagnostic marker”获取最新研究。
The INSM1 (Insulinoma-associated protein 1) antibody is a valuable tool in studying and diagnosing neuroendocrine neoplasms. INSM1. a zinc-finger transcription factor, plays a critical role in neuroendocrine differentiation and embryonic development, particularly in the nervous system, pancreas, and endocrine tissues. First identified in insulinomas, it is highly expressed during embryogenesis but largely silenced in most adult tissues, except in neuroendocrine cells. Reactivation of INSM1 has been observed in various neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), including small cell lung carcinoma, medullary thyroid cancer, and neuroblastoma, making it a specific biomarker for these malignancies.
The INSM1 antibody detects nuclear expression of the INSM1 protein via immunohistochemistry (IHC) or immunofluorescence. Its clinical utility stems from high sensitivity and specificity for NETs, often outperforming traditional markers like chromogranin A and synaptophysin, especially in poorly differentiated cases. Additionally, it aids in distinguishing NETs from non-neuroendocrine cancers, supporting accurate classification and treatment planning. Research also employs INSM1 antibodies to explore developmental biology, tumorigenesis mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targets. Overall, INSM1 antibodies bridge diagnostic precision and molecular research in neuroendocrine pathology.
×