| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
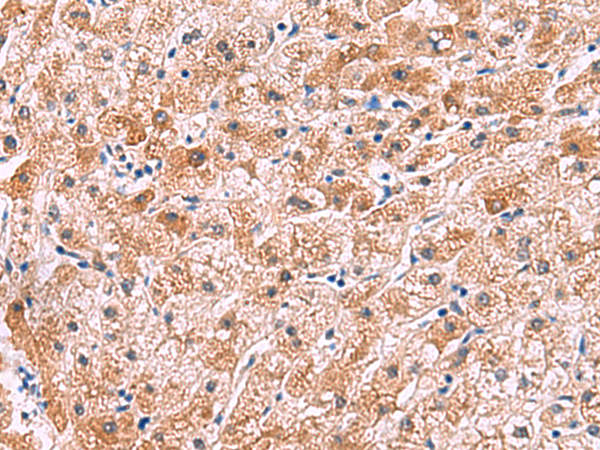
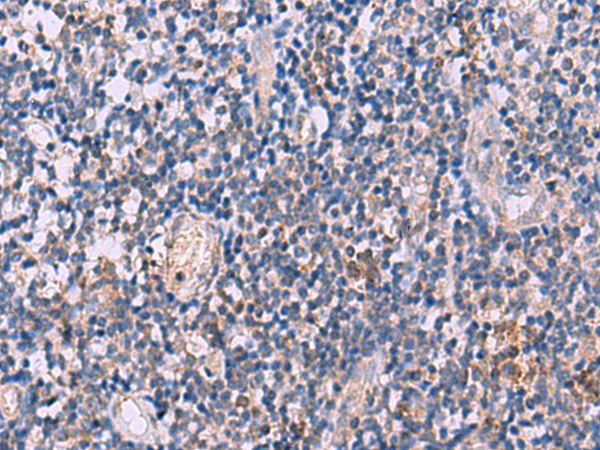
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD124; IL4RA; IL-4RA |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human IL4R |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IL4R抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要:
1. **"Dupilumab in Persistent Asthma with Elevated Eosinophil Levels" (Wenzel S et al., NEJM, 2013)**
摘要:研究评估抗IL4Rα单抗dupilumab在中重度哮喘患者中的疗效。结果显示,与安慰剂相比,dupilumab显著减少哮喘急性发作并改善肺功能,尤其对嗜酸性粒细胞水平升高的患者效果显著。
2. **"IL-4 Receptor α Blockade Prevents Airway Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Asthma" (Oh CK et al., J Immunol, 2010)**
摘要:通过小鼠模型研究抗IL4Rα抗体对哮喘气道炎症的作用。实验表明,阻断IL-4Rα可抑制Th2细胞反应、黏液分泌及嗜酸性粒细胞浸润,为靶向IL4R治疗哮喘提供机制支持。
3. **"Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety in Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis" (Simpson EL et al., JAMA Dermatol, 2016)**
摘要:III期临床试验证实,dupilumab可显著改善中重度特应性皮炎患者的皮损和瘙痒症状,且安全性良好,支持IL4Rα作为治疗靶点的有效性。
4. **"Targeting IL-4/IL-13 Signaling in Allergic Diseases" (Gandhi NA et al., Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2017)**
摘要:综述IL4R下游的IL-4/IL-13通路在过敏性疾病中的作用,强调抗IL4R抗体通过双重抑制该通路调控炎症反应,总结其在特应性皮炎、哮喘等疾病中的临床进展。
The interleukin-4 receptor (IL-4R) is a cell-surface protein that plays a central role in regulating immune responses, particularly those mediated by type 2 helper T (Th2) cells. It exists in two forms: Type I (IL-4Rα paired with the common gamma chain γc) binds IL-4. while Type II (IL-4Rα combined with IL-13Rα1) interacts with both IL-4 and IL-13. These cytokines drive allergic inflammation by promoting B-cell activation, IgE production, eosinophil recruitment, and tissue remodeling. Dysregulated IL-4R signaling is implicated in Th2-mediated diseases such as asthma, atopic dermatitis, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, and eosinophilic esophagitis.
Targeting IL-4Rα with monoclonal antibodies offers a strategic approach to block signaling from both IL-4 and IL-13. Dupilumab, the first FDA-approved IL-4Rα antibody (2017), demonstrates efficacy in multiple allergic and type 2 inflammatory conditions by inhibiting downstream pathways like JAK-STAT. Other candidates, including tralokinumab, have shown more limited success, highlighting the complexity of cytokine redundancy in these diseases. Emerging research explores IL-4R blockade in fibrotic disorders and cancer immunotherapy, where IL-4/IL-13 may suppress antitumor immunity. While generally well-tolerated, long-term safety profiles and predictive biomarkers for treatment response remain active investigation areas. The dual cytokine inhibition strategy positions IL-4R antibodies as versatile tools for modulating Th2-driven pathology.
×