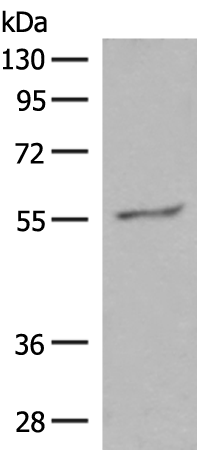
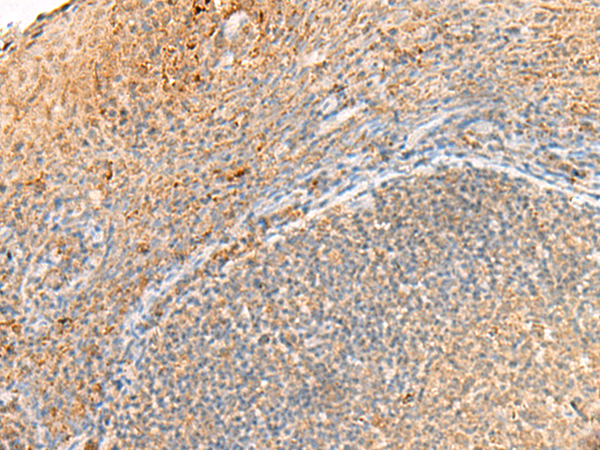
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RE2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 59 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GPR161 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GPR161抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*GPR161 controls retinal progenitor cell fate through Hedgehog signaling*
**作者**:Mukhopadhyay, S. et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了GPR161在视网膜发育中的关键作用,通过调控Hedgehog信号通路影响神经前体细胞分化。研究利用特异性GPR161抗体进行免疫染色,证实其在视网膜中的定位及与Hedgehog通路抑制因子SUFU的相互作用。
2. **文献名称**:*GPR161 regulates skin tumorigenesis by modulating immune cell infiltration*
**作者**:Shimada, I.S. et al.
**摘要**:文章探讨GPR161在皮肤癌中的免疫调节功能。通过Western blot和免疫组化(使用GPR161抗体),发现GPR161缺失导致肿瘤微环境中免疫细胞募集减少,提示其通过cAMP信号通路影响肿瘤进展。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural insights into GPR161 function and ciliary localization*
**作者**:Niewiadomski, P. et al.
**摘要**:研究解析了GPR161在纤毛中的结构及功能机制。利用定制GPR161抗体验证其纤毛定位,并揭示其通过调节环磷酸腺苷(cAMP)水平参与Hedgehog信号通路的负向调控。
4. **文献名称**:*GPR161 mutations disrupt brain development and cause Joubert syndrome*
**作者**:Pal, K. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次将GPR161突变与Joubert综合征相关联。通过患者样本和小鼠模型,结合GPR161抗体的免疫荧光分析,发现突变导致纤毛信号异常及脑部发育缺陷,强调了其在神经发育中的必要性。
以上文献均通过GPR161抗体进行蛋白定位、表达分析或功能验证,聚焦于其在发育、疾病及分子机制中的作用。
**Background of GPR161 Antibody**
GPR161 (G protein-coupled receptor 161) is an orphan receptor belonging to the class A G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. It is evolutionarily conserved and plays a critical role in regulating Hedgehog (Hh) signaling, a pathway essential for embryonic development and tissue homeostasis. GPR161 is predominantly localized to primary cilia, where it constitutively activates Gαs-mediated cAMP signaling, suppressing Hh pathway activity. Its dysfunction has been linked to developmental disorders and cancers, particularly medulloblastoma and basal cell carcinoma.
Antibodies targeting GPR161 are vital tools for studying its expression, subcellular localization, and functional mechanisms. They are commonly used in techniques like immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, and immunofluorescence (IF) to assess protein levels in tissues or cultured cells. Many commercially available GPR161 antibodies are raised against specific epitopes, such as the N-terminal extracellular or C-terminal intracellular regions, ensuring specificity for detecting endogenous or overexpressed proteins.
Research utilizing GPR161 antibodies has revealed its downregulation in certain tumors, suggesting a tumor-suppressive role. Additionally, studies in knockout models highlight its importance in neural tube development and craniofacial morphogenesis. As an orphan receptor, GPR161’s ligand and precise signaling cascades remain under investigation, making reliable antibodies crucial for advancing its biological and pathological characterization.
×