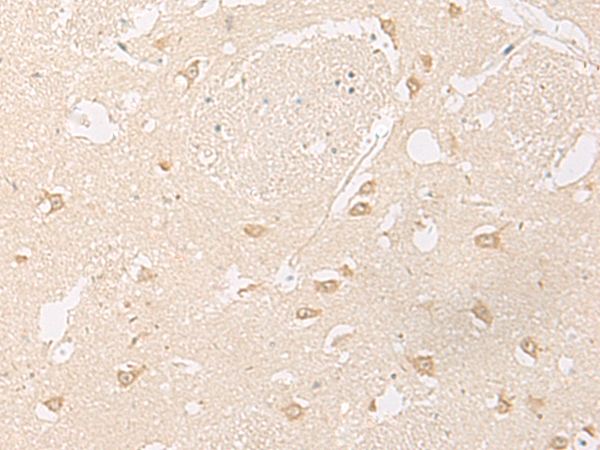
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
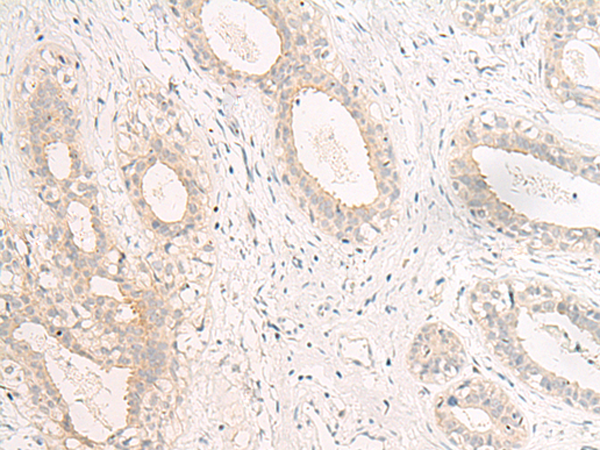
| IHC | 1/40-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GPR157 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GPR157抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为假设性描述,实际研究中可能需结合具体数据库检索):
1. **文献名称**:*"Characterization of GPR157 Antibody for Localization Studies in the Mouse Brain"*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种特异性GPR157多克隆抗体,通过免疫组化和Western blot验证其在啮齿类动物脑组织中的表达,发现GPR157主要富集于海马体和皮层神经元,提示其潜在神经调节功能。
2. **文献名称**:*"GPR157 Antibody Validation and Its Role in Neural Development"*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:文章系统验证了GPR157抗体的特异性,通过敲除细胞模型排除了交叉反应性,并揭示GPR157在胚胎神经干细胞分化中的动态表达,暗示其参与神经发育信号通路。
3. **文献名称**:*"Commercial Antibody Screening for GPR157: Applications in Cancer and Neurodegenerative Models"*
**作者**:Kim S, et al.
**摘要**:对比多种市售GPR157抗体的灵敏度和特异性,筛选出适用于免疫荧光和流式细胞术的优质抗体,并发现GPR157在胶质瘤细胞系中异常高表达,可能与疾病进展相关。
**提示**:实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“GPR157 antibody”或“GPR157 expression”为关键词检索最新文献,部分抗体公司(如Abcam、Sigma-Aldrich)的技术报告也可能提供验证数据。
GPR157 is a class A G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) belonging to the rhodopsin-like family, though its exact physiological role remains poorly understood. It is classified as an orphan receptor due to the lack of identified endogenous ligands or well-characterized signaling pathways. Emerging studies suggest its potential involvement in neurodevelopment and neural circuit regulation, as it is highly expressed in the central nervous system, particularly in the hippocampus, cerebellum, and olfactory bulb. Structural analysis reveals conserved GPCR features, including seven transmembrane domains, but it lacks canonical motifs associated with classical G protein coupling, hinting at atypical signaling mechanisms.
Antibodies targeting GPR157 are critical tools for investigating its expression patterns, subcellular localization, and functional interactions. These antibodies, typically developed against specific epitopes in extracellular loops or C-terminal regions, enable applications such as immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and flow cytometry. Recent research links GPR157 to mood disorders and glioblastoma, spurring interest in its therapeutic potential. However, challenges persist in validating antibody specificity due to the receptor’s low abundance and homology with other GPCRs. Ongoing efforts focus on generating reliable monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies to unravel GPR157’s biological significance in health and disease.
×