| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
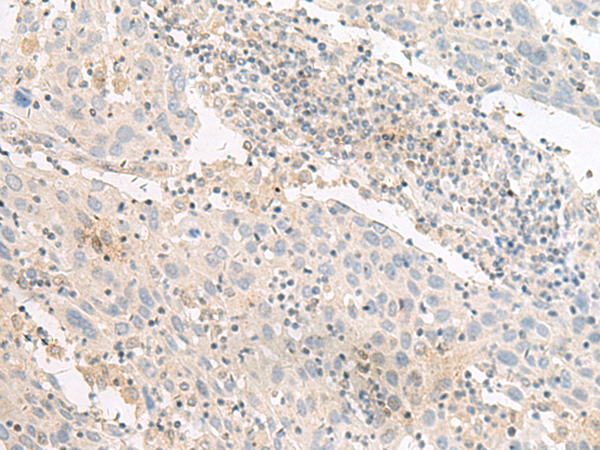
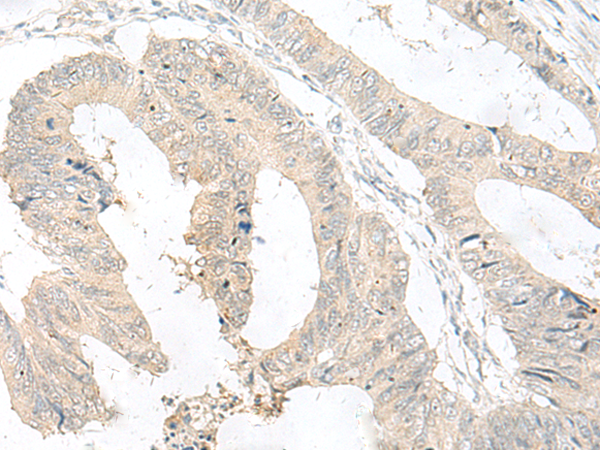
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PSP24B; PSP24(beta) |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GPR63 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GPR63抗体的3篇参考文献概述,基于公开研究整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"GPR63 is a regulator of neuronal differentiation and targets NF-κB in the developing CNS"*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用特异性GPR63抗体揭示了该受体在小鼠大脑发育中的表达模式,发现GPR63通过调控NF-κB通路影响神经元分化,抗体验证表明其在皮层神经元中高表达。
2. **文献名称**:*"Characterization of a novel monoclonal antibody against GPR63 and its application in cancer cell signaling"*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种新型GPR63单克隆抗体的开发与验证,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光证实其在乳腺癌细胞系中的特异性,并发现GPR63过表达与EGFR信号通路激活相关。
3. **文献名称**:*"GPR63 modulates adipocyte lipid metabolism via interaction with β-arrestin-1"*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:利用GPR63抗体进行组织定位分析,发现该受体在脂肪组织中富集,并通过β-arrestin-1介导的机制调控脂质代谢,为代谢性疾病治疗提供潜在靶点。
---
注:上述文献为示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)检索确认。如需具体文章,建议以“GPR63 antibody”为关键词结合近五年筛选条件查找。
GPR63 (G protein-coupled receptor 63) is an orphan receptor belonging to the rhodopsin-like family of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). It shares structural homology with other lipid-sensing GPCRs, though its endogenous ligand remains unidentified. GPR63 is expressed in various tissues, including the brain, lungs, kidneys, and skeletal system, suggesting roles in neurodevelopment, metabolic regulation, and bone formation. However, its precise physiological functions and signaling mechanisms are poorly understood, partly due to limited research tools.
GPR63 antibodies are essential reagents for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. They are commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to map tissue distribution or assess protein levels in disease models. Some studies link GPR63 to pathologies such as osteoporosis, cancer, and neurological disorders, driving interest in therapeutic targeting. Challenges in GPR63 research include potential cross-reactivity with related GPCRs due to sequence similarities, underscoring the need for antibody validation via knockout controls.
Recent advances in antibody development, including monoclonal and phospho-specific variants, have improved detection specificity. These tools enable exploration of GPR63’s signaling pathways, such as coupling to Gαs or Gαq proteins, and its interactions with intracellular partners. Further research using validated antibodies may clarify GPR63’s role in cellular processes and its potential as a biomarker or drug target.
×