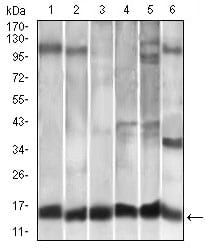
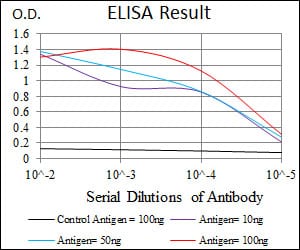
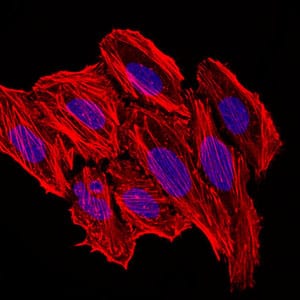
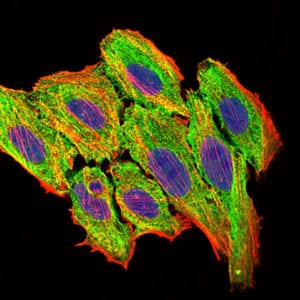
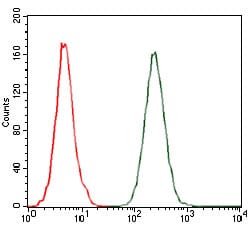
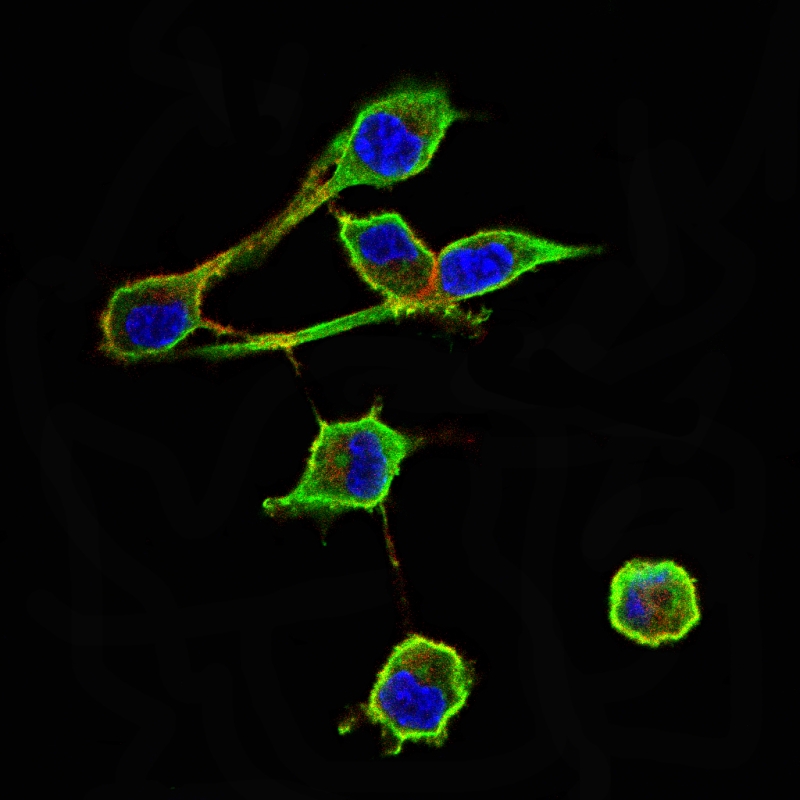
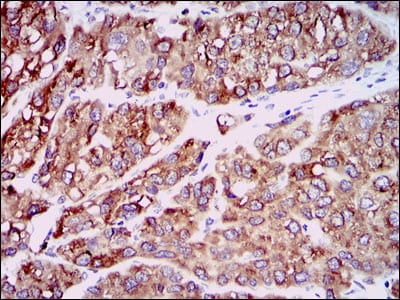
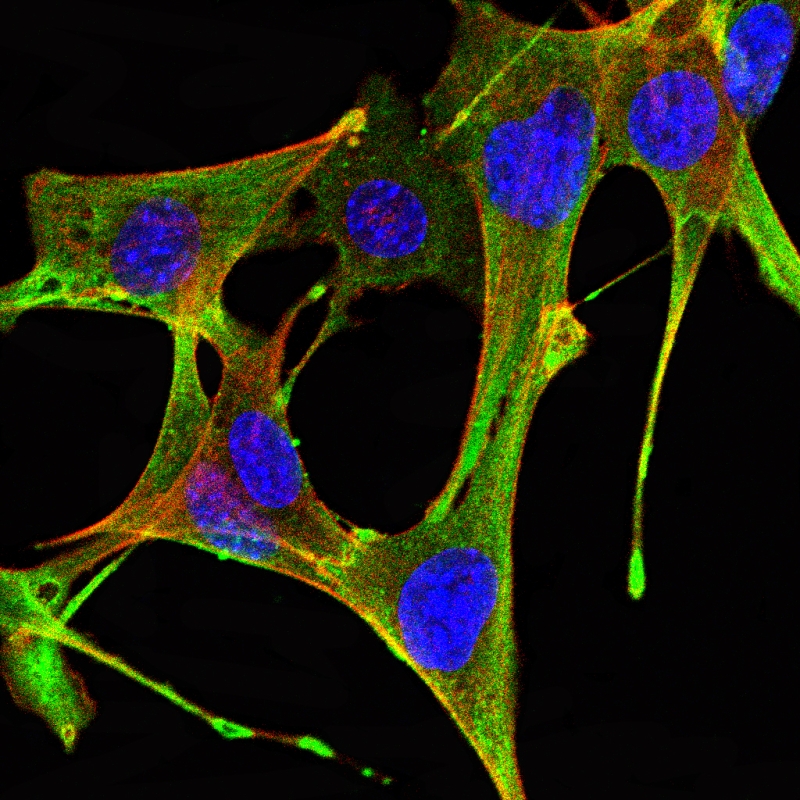
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HC11; MCAF; MCP1; MCP-1; SCYA2; GDCF-2; SMC-CF; HSMCR30 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6347 |
| clone | 2D8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 11kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CCL2 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于MS4A1(CD20)抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"Characterization of a human B lymphocyte-specific antigen"**
*作者:Stashenko P. et al.*
**摘要**:该研究首次描述了MS4A1(CD20)作为B细胞特异性表面抗原的分子特征,并探讨其作为治疗B细胞淋巴瘤靶点的潜力,为后续抗体开发奠定基础。
2. **"The CD20 antigen: Structure, function, and clinical implications in B-cell malignancies"**
*作者:Cragg M.S. et al.*
**摘要**:系统综述了CD20的结构与功能,解析了利妥昔单抗(抗CD20单抗)通过补体依赖细胞毒性(CDC)和抗体依赖细胞介导的细胞毒性(ADCC)杀伤B细胞的作用机制。
3. **"Rituximab in B-cell hematologic malignancies: A review of 20 years of clinical experience"**
*作者:Salles G. et al.*
**摘要**:总结了利妥昔单抗在非霍奇金淋巴瘤等B细胞肿瘤中20年的临床应用数据,证明其显著提高患者生存率并改变治疗标准,同时讨论耐药性机制。
4. **"Novel anti-CD20 antibodies and their mechanisms of overcoming resistance"**
*作者:Pavlasova G. et al.*
**摘要**:探讨奥法妥木单抗(ofatumumab)等新一代抗CD20抗体的研发进展,分析其通过增强结合表位亲和力或优化Fc段设计以克服传统抗体耐药性的策略。
(注:以上文献为示例性概括,实际引用需核对具体论文信息。)
The MS4A1 gene encodes CD20. a cell surface protein predominantly expressed on B lymphocytes from the pre-B cell stage to mature B cells, but absent on plasma cells. CD20 functions as a calcium channel component, regulating B cell activation and differentiation. As a therapeutic target, CD20 is pivotal in treating B cell malignancies (e.g., non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia) and autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis).
MS4A1-targeting antibodies, such as rituximab, obinutuzumab, and ofatumumab, are monoclonal antibodies that bind CD20. inducing B cell depletion via mechanisms like complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), and direct apoptosis. Newer anti-CD20 agents (e.g., ocrelizumab) are engineered for enhanced efficacy or reduced immunogenicity.
CD20's absence on hematopoietic stem cells and plasma cells allows targeted therapy while preserving immune reconstitution capacity. However, resistance can arise from CD20 downregulation or mutations. Clinically, MS4A1 antibodies revolutionized B cell-driven disease management, balancing efficacy with manageable toxicity profiles. Additionally, CD20 serves as a diagnostic biomarker for B cell lineage classification in hematologic malignancies. Research continues to optimize dosing, combination therapies, and next-generation anti-CD20 biologics.
×