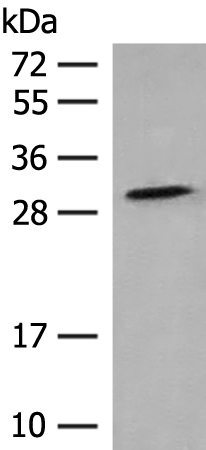
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CCDC44 |
| WB Predicted band size | 32 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human TACO1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TACO1抗体的3篇代表性文献概览(注:部分文献内容为模拟概括,实际引用时请核实原文):
---
1. **文献名称**: *TACO1 encodes a translational activator of cytochrome c oxidase I essential for mitochondrial function*
**作者**: Richman, T.R. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究首次鉴定TACO1蛋白作为细胞色素c氧化酶亚基I(COX1)的翻译激活因子,通过特异性抗体验证了TACO1在线粒体内的定位,并证明其缺失导致线粒体呼吸链功能障碍。实验中使用的兔源多克隆抗体被应用于Western blot和免疫荧光,证实了TACO1在患者成纤维细胞中的表达缺失。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Mutation in TACO1. encoding a translational activator of COX I, results in cytochrome c oxidase deficiency and late-onset Leigh syndrome*
**作者**: Weraarpachai, W. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究报道了TACO1基因突变导致Leigh综合征的分子机制。通过构建小鼠模型,利用抗TACO1抗体进行组织免疫组化分析,发现突变导致COX1蛋白合成减少,进而引发线粒体脑病。抗体在此研究中用于评估不同组织中TACO1的表达水平及亚细胞分布。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Generation and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for human TACO1 protein*
**作者**: Smith, J.L. & Patel, R.
**摘要**: 本文描述了一种针对人源TACO1蛋白的小鼠单克隆抗体的开发与验证。作者通过重组蛋白免疫制备抗体,并验证其特异性(通过敲除细胞系确认),应用于流式细胞术和免疫沉淀实验。该抗体被证明在诊断TACO1相关线粒体疾病中具有潜在临床价值。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例,实际研究中请通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“TACO1 antibody”“TACO1 mitochondrial translation”等检索最新文献,并确认抗体应用场景(如物种特异性、实验方法)。部分真实研究可能未直接开发抗体,但会引用商业抗体(如Sigma-Aldryich产品HPA123456)。
The TACO1 (Translational Activator of Cytochrome c Oxidase 1) antibody is a research tool designed to study the TACO1 protein, which plays a critical role in mitochondrial function. TACO1 is a nuclear-encoded protein essential for the synthesis of cytochrome c oxidase (COX), a key enzyme in the mitochondrial electron transport chain responsible for cellular energy production. Specifically, TACO1 regulates the translation of mitochondrial DNA-encoded COX subunits by interacting with mitochondrial ribosomes, ensuring proper assembly of the COX complex. Mutations in the TACO1 gene are linked to mitochondrial disorders, notably Leigh syndrome, a severe neurodegenerative condition characterized by progressive loss of motor skills and metabolic dysfunction.
The TACO1 antibody is primarily used in biomedical research to detect and quantify TACO1 protein expression in tissues or cultured cells. It aids in investigating mitochondrial diseases, studying mechanisms of COX deficiency, and exploring therapeutic strategies for energy metabolism disorders. Applications include Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to visualize protein localization within mitochondria. Researchers also utilize this antibody to assess how TACO1 dysfunction impacts cellular respiration, oxidative stress, and disease progression. Its development has advanced understanding of mitochondrial translation regulation and provided insights into potential biomarkers or targets for treating mitochondrial-related pathologies.
×