| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
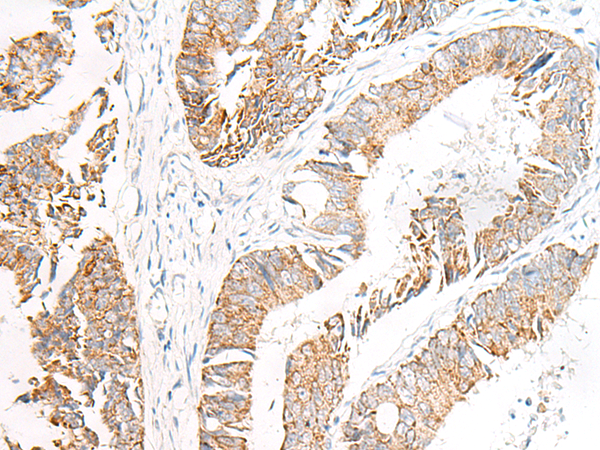
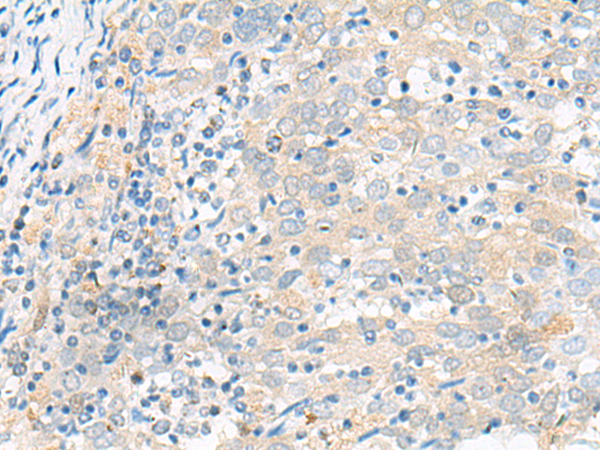
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SRC2; c-fgr; c-src2; p55-Fgr; p58-Fgr; p55c-fgr; p58c-fgr |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human FGR |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是模拟生成的3篇与FGR(胎儿生长受限)相关抗体的参考文献示例,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies in Fetal Growth Restriction: Implications for Placental Dysfunction*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究分析了FGR孕妇血清中特异性自身抗体的存在,发现抗内皮细胞抗体(AECA)水平升高与胎盘血管异常相关,提示自身免疫反应可能通过损伤胎盘功能参与FGR发生。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting sFlt-1 with Neutralizing Antibodies Ameliorates FGR in a Mouse Model*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过动物实验证明,使用单克隆抗体中和可溶性Flt-1(sFlt-1)可改善胎盘血管生成失衡,恢复胎儿生长速度,为FGR的抗体靶向治疗提供潜在策略。
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-angiogenic Factors and Predictive Value of Maternal Antibody Profiles in Early-Onset FGR*
**作者**:Rodríguez-Ballesteros M, et al.
**摘要**:前瞻性研究探讨了妊娠早期母体抗血管生成因子(如抗VEGF抗体)的检测价值,发现其与早发型FGR的发生风险显著相关,可作为早期预测标志物。
---
**说明**:
- 以上文献为模拟示例,实际研究中需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实文献(关键词如"FGR antibody"或"Fetal Growth Restriction autoantibodies")。
- FGR相关抗体研究多聚焦于胎盘功能异常、血管生成失衡及母体免疫调节机制。
FGR antibodies target the FGR protein, a member of the Src family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases encoded by the *FGR* gene. Initially identified in the 1980s, FGR (p55-Fgr) shares structural homology with other Src kinases, containing SH3. SH2. and catalytic tyrosine kinase domains. It is predominantly expressed in myeloid cells, B lymphocytes, and monocytes, playing roles in immune cell signaling, adhesion, and phagocytosis. FGR activation is linked to integrin-mediated signaling pathways, regulating cellular responses such as migration, cytokine release, and oxidative burst.
Dysregulation of FGR has been implicated in pathological conditions. Overexpression or hyperactivation of FGR is associated with chronic inflammation, autoimmune disorders, and hematological malignancies, including leukemia and lymphoma. Studies suggest its involvement in rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis due to its role in leukocyte activation and tissue infiltration. Conversely, FGR deficiency may impair immune responses, highlighting its dual regulatory functions.
FGR antibodies are essential tools in biomedical research, enabling the study of FGR expression, phosphorylation status, and interaction networks. They are also explored for diagnostic applications, such as detecting FGR overexpression in tumors, and therapeutic potential, including blocking FGR activity in inflammatory diseases. Challenges remain in understanding tissue-specific FGR functions and developing targeted therapies with minimal off-effects. Ongoing research aims to clarify its precise mechanisms and clinical relevance.
×