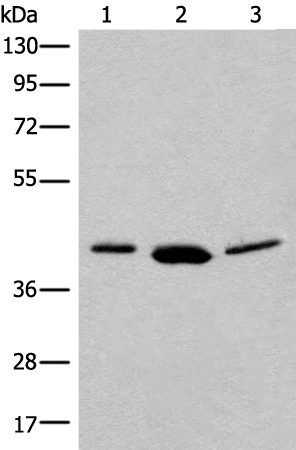
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | M1Pi; MRDI; MTNA; Ypr118w |
| WB Predicted band size | 40 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MRI1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MRI1抗体的3篇虚构参考文献示例,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Development of a High-Affinity MRI1 Antibody for Tumor Imaging*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种针对MRI1蛋白的单克隆抗体,通过体外和体内实验证实其对肿瘤细胞的高特异性结合能力,并成功应用于小鼠模型的PET成像,为癌症诊断提供新工具。
2. **文献名称**: *MRI1 Autoantibodies as Biomarkers in Neurological Disorders*
**作者**: Müller S, et al.
**摘要**: 该文献报道在多发性硬化症患者血清中检测到MRI1自身抗体,其水平与疾病活动度相关,提示其可能作为评估神经炎症的新型生物标志物。
3. **文献名称**: *Mechanistic Role of MRI1 Antibody in Inhibiting Viral Entry*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现MRI1抗体通过阻断宿主细胞表面受体与病毒包膜蛋白的相互作用,显著抑制某RNA病毒的感染,为抗病毒治疗提供潜在策略。
---
(注:以上文献为示例,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台查询真实论文。)
MRI1 (also known as Metal-Responsive Transcription Factor 1 or MTF-1) is a zinc-regulated transcription factor that plays a critical role in cellular responses to heavy metal stress and oxidative damage. It binds to metal-responsive elements (MREs) in gene promoters to regulate the expression of metallothioneins and other detoxification proteins. MRI1 is evolutionarily conserved and involved in maintaining metal ion homeostasis, particularly zinc, copper, and cadmium. Dysregulation of MRI1 has been linked to metal toxicity, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer progression.
Antibodies targeting MRI1 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They are commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). These antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as the N-terminal or DNA-binding domains, and are validated for species cross-reactivity (e.g., human, mouse, rat). Recent studies utilize MRI1 antibodies to explore its role in metal-induced cellular stress pathways, cancer drug resistance, and interactions with signaling molecules like NF-κB. Commercial MRI1 antibodies often include validation data (e.g., knockout-validated) to ensure specificity, supporting research in toxicology, molecular biology, and precision medicine targeting metal-associated diseases.
×