| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
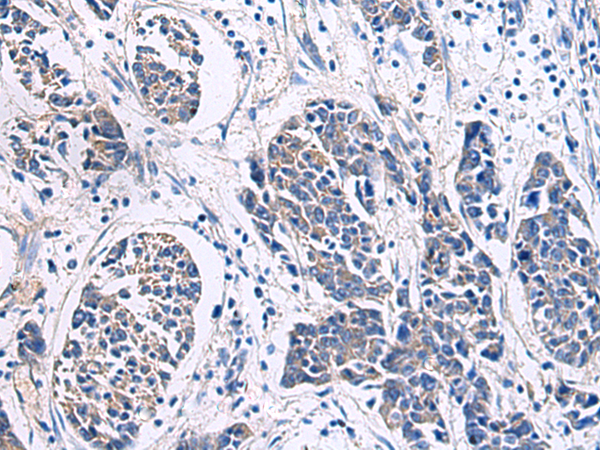
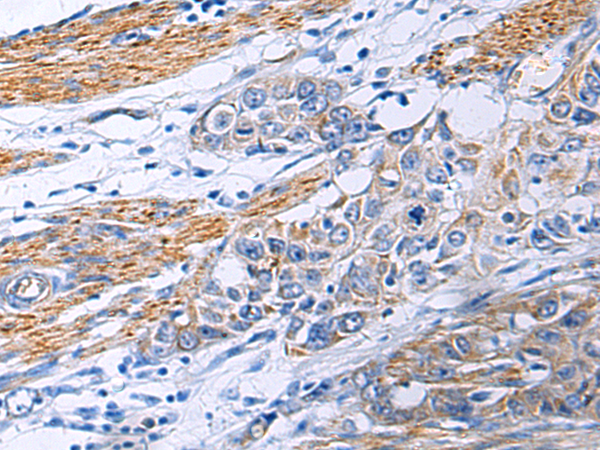
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PRO0327 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human POLQ |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与POLQ抗体相关的文献摘要示例:
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting DNA polymerase θ in cancer therapy*
**作者**:Ceccaldi, R. et al.
**摘要**:研究证明POLQ在多种癌症中高表达,其抗体用于检测肿瘤细胞中POLQ蛋白水平,并验证抑制POLQ可增强放疗敏感性,为靶向治疗提供依据。
2. **文献名称**:*POLQ inhibition suppresses BRCA-deficient tumor progression*
**作者**:Higgins, G.S. & Boulton, S.J.
**摘要**:利用POLQ抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现BRCA突变肿瘤依赖POLQ介导的DNA修复。抑制POLQ联合PARP抑制剂可协同杀伤肿瘤细胞。
3. **文献名称**:*A synthetic lethal approach targeting POLQ in homologous recombination-deficient cancers*
**作者**:Feng, W. et al.
**摘要**:通过POLQ抗体验证基因敲除效率,研究显示POLQ缺失导致TMEJ功能丧失,显著抑制HR缺陷型肿瘤生长,提示其作为合成致死靶点的潜力。
4. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody specific for human POLQ*
**作者**:Ko, H.L. & Ren, E.C.
**摘要**:报道一种高特异性抗人POLQ单克隆抗体的开发,验证其在流式细胞术和免疫荧光中的应用,为POLQ表达定量及亚细胞定位提供工具。
(注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需以具体论文为准。)
POLQ (DNA polymerase theta) is a specialized DNA polymerase involved in an error-prone DNA repair pathway known as theta-mediated end joining (TMEJ), which serves as a backup mechanism for repairing double-strand breaks (DSBs) when canonical repair pathways like homologous recombination (HR) are compromised. Discovered in the early 2000s, POLQ gained attention for its unique ability to mediate microhomology-based DNA repair, often resulting in genomic rearrangements. Its expression is generally low in healthy tissues but upregulated in various cancers, particularly those with defects in HR (e.g., BRCA-mutant cancers), where POLQ supports cancer cell survival by mitigating replication stress and repairing therapy-induced DNA damage.
POLQ antibodies are critical tools for studying its biological roles, including its localization, expression levels, and interaction partners in cancer models. Researchers have linked elevated POLQ levels to poor prognosis, chemoresistance, and radioresistance in cancers such as breast, ovarian, and lung adenocarcinoma. These findings spurred interest in POLQ as a therapeutic target, with inhibitors (including antibody-based strategies) currently in preclinical development. POLQ inhibition is hypothesized to synergize with DNA-damaging therapies or PARP inhibitors, selectively targeting HR-deficient cancers. However, challenges remain in optimizing specificity and minimizing off-target effects. Overall, POLQ antibodies continue to advance both basic research and translational efforts in oncology.
×