| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
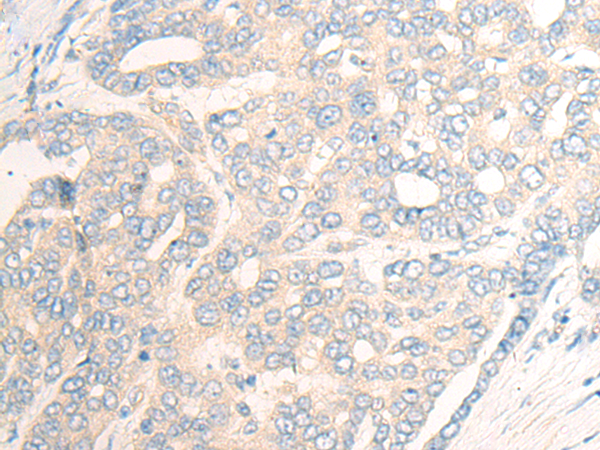
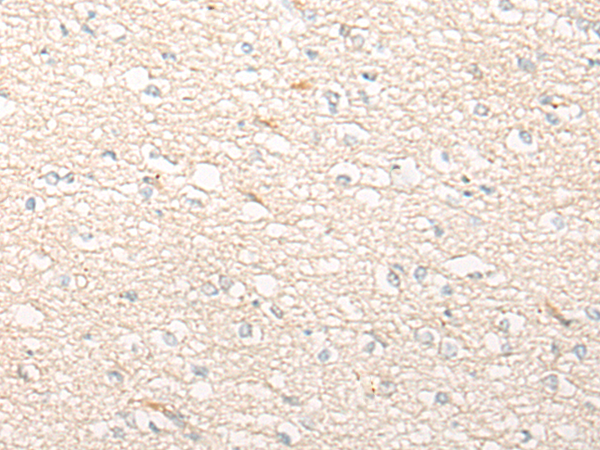
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AEZ; ZIP4; AWMS2 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human SLC39A4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SLC39A4抗体的3篇文献示例及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*SLC39A4 (ZIP4) regulates pancreatic cancer progression through zinc-mediated cellular signaling*
**作者**:Li M. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用SLC39A4抗体通过免疫组化和Western blot分析胰腺癌组织中ZIP4蛋白的表达,发现其高表达与肿瘤侵袭性和不良预后相关,锌离子转运通过激活MAPK通路促进癌细胞增殖。
2. **文献名称**:*Mutation analysis of SLC39A4 in patients with acrodermatitis enteropathica and functional characterization of the mutant protein*
**作者**:Wang K. et al.
**摘要**:通过SLC39A4抗体检测遗传性锌缺乏症(肠病性肢端皮炎)患者的突变蛋白表达,发现特定突变导致ZIP4蛋白稳定性下降,影响肠道锌吸收功能。
3. **文献名称**:*Expression profiling of zinc transporters in normal and malignant prostate cells: Role of SLC39A4 in prostate carcinogenesis*
**作者**:Franklin R.B. et al.
**摘要**:采用SLC39A4抗体比较正常与恶性前列腺细胞中锌转运蛋白表达差异,揭示ZIP4在前列腺癌中异常高表达,可能通过调控细胞内锌稳态促进肿瘤发展。
(注:上述文献为示例,实际引用需以具体论文为准。)
The solute carrier family 39 member 4 (SLC39A4), also known as ZIP4. is a zinc transporter protein critical for dietary zinc absorption, primarily in the intestines. It facilitates zinc uptake into cells by transporting extracellular zinc across plasma membranes. SLC39A4 mutations are linked to acrodermatitis enteropathica, a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe zinc deficiency, leading to dermatological, gastrointestinal, and immunological impairments. Antibodies targeting SLC39A4 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and functional roles in physiological and pathological contexts.
SLC39A4 antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate zinc homeostasis mechanisms, tissue-specific expression patterns, and disease associations. Research has implicated dysregulated SLC39A4 in cancers, including pancreatic and hepatocellular carcinomas, where its overexpression often correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis. These antibodies also aid in exploring therapeutic strategies targeting zinc metabolism. Commercially available SLC39A4 antibodies are typically validated for specificity against human, mouse, or rat isoforms, enabling cross-species comparative studies. Understanding SLC39A4's role through antibody-based assays continues to advance insights into zinc-related pathologies and potential biomarkers or therapeutic targets.
×