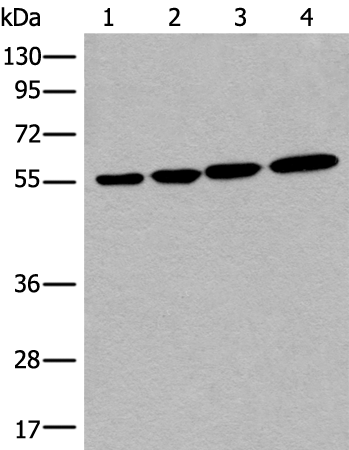
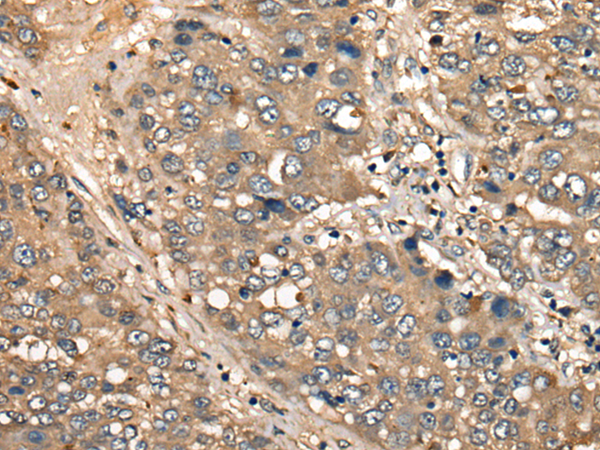
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B7H3; B7-H3; B7RP-2; 4Ig-B7-H3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 57 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CD276 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD276抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*B7-H3 as a Target for Cancer Immunotherapy*
**作者**:Prasad D.V.R. 等
**摘要**:探讨CD276(B7-H3)在肿瘤免疫逃逸中的作用,提出其作为免疫治疗靶点的潜力,并总结靶向抗体在抑制肿瘤生长及增强T细胞活性中的实验效果。
2. **文献名称**:*CD276 Antibody-Drug Conjugate for Targeted Prostate Cancer Therapy*
**作者**:Seaman S. 等
**摘要**:开发了一种靶向CD276的抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),在临床前模型中显示可通过特异性结合肿瘤细胞并释放细胞毒素,显著抑制前列腺癌进展。
3. **文献名称**:*B7-H3-Specific CAR-T Cells Exhibit Potent Activity Against Pediatric Solid Tumors*
**作者**:Majzner R.G. 等
**摘要**:研究利用CD276特异性CAR-T细胞治疗儿童实体瘤的疗效,结果显示其在小鼠模型中有效清除肿瘤细胞,并验证了CD276在多种儿科肿瘤中的高表达特性。
4. **文献名称**:*Dual Role of B7-H3 in Tumor Immunity*
**作者**:Chapoval A.I. 等
**摘要**:分析CD276在肿瘤微环境中的双重功能,既可能抑制T细胞应答,又参与促血管生成;提出靶向抗体需结合具体肿瘤类型设计治疗策略。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用需根据具体论文核实。)
CD276. also known as B7-H3. is a member of the B7 immune checkpoint protein family, involved in regulating T-cell-mediated immune responses. It is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed at low levels in normal tissues but often overexpressed in various cancers, including lung, breast, prostate, and glioblastoma. Its dual role in immune modulation—both co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory—has sparked interest in its potential as a therapeutic target. CD276's overexpression in tumors correlates with immune evasion, poor prognosis, and resistance to therapies, making it a focus for cancer immunotherapy.
CD276 antibodies are designed to block its immunosuppressive signaling or deliver targeted therapies. Preclinical studies suggest that anti-CD276 antibodies enhance anti-tumor immunity by reactivating T-cell activity or through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Additionally, CD276-targeting antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and CAR-T cells are under investigation to exploit its tumor-selective expression. Despite promise, challenges remain, including understanding CD276's precise receptor interactions and balancing efficacy with potential on-target, off-tumor toxicity due to its low-level expression in healthy tissues. Ongoing clinical trials aim to validate its therapeutic utility in combination with existing immunotherapies.
×