
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
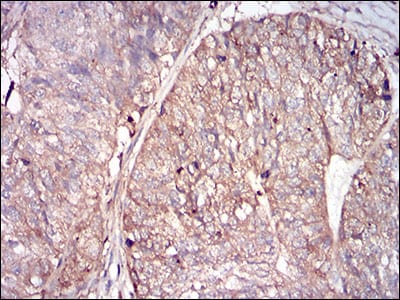
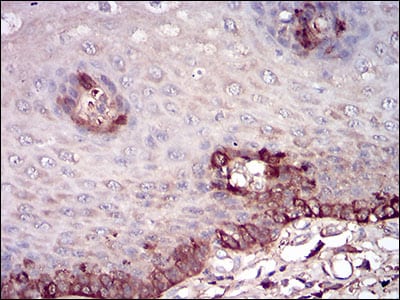
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
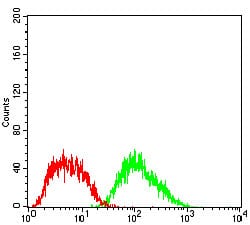
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
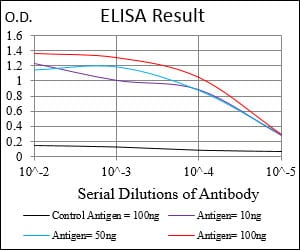
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NBIA3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2512 |
| clone | 6E10E4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 20kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human FTL (AA: FULL(1-175)) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于HOOK2抗体的3篇参考文献概览:
1. **文献名称**:*HOOK2 regulates cilium formation and autophagy through interaction with PCM1*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用HOOK2抗体进行免疫共沉淀和免疫荧光实验,发现HOOK2通过与PCM1蛋白互作调控初级纤毛形成,并影响自噬通路,揭示了其在细胞器动态平衡中的作用。
2. **文献名称**:*HOOK2 deficiency causes mitochondrial dysfunction and ciliopathy-like phenotypes in mice*
**作者**:Chen J, et al.
**摘要**:通过HOOK2抗体检测基因敲除小鼠模型,证实HOOK2缺失导致线粒体膜电位异常和纤毛结构缺陷,提示其与遗传性纤毛疾病的相关性。
3. **文献名称**:*HOOK2 anchors the dynein complex to the Golgi for efficient vesicle transport*
**作者**:Schroeder CM, et al.
**摘要**:研究采用HOOK2抗体进行超分辨成像,证明HOOK2作为动力蛋白复合体的锚定点,介导高尔基体衍生囊泡的微管依赖性运输,影响分泌途径效率。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核对具体来源及DOI编号。)
The HOOK2 antibody is a valuable tool in studying the HOOK family of proteins, which play critical roles in intracellular trafficking processes. HOOK2. a member of the HOOK protein family (HOOK1. HOOK2. HOOK3), acts as an adaptor protein that links organelles to microtubules, facilitating vesicular transport and organelle positioning. It is structurally characterized by an N-terminal microtubule-binding domain, a central coiled-coil region, and a C-terminal domain that interacts with cargo-specific proteins. HOOK2 is particularly implicated in endosomal trafficking, Golgi organization, and ciliogenesis, where it collaborates with molecular partners like FTS (Fused Toes) and RUN domain proteins to regulate cargo movement along microtubules.
Research using HOOK2 antibodies has highlighted its functional significance in diverse cellular processes, including receptor recycling, lysosomal biogenesis, and centrosome cohesion. Dysregulation of HOOK2 expression or mutations are associated with pathological conditions such as ciliopathies, neurodevelopmental disorders, and cancers. For instance, reduced HOOK2 levels correlate with defective cilia formation, contributing to renal or retinal diseases. In cancer, altered HOOK2 expression may influence cell migration and metastasis via disrupted intracellular transport.
HOOK2-specific antibodies enable the detection and localization of endogenous HOOK2 in cells and tissues through techniques like Western blot, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. These reagents are essential for exploring HOOK2's molecular interactions, post-translational modifications, and tissue-specific expression patterns, providing insights into its physiological and pathological roles across species, including humans and model organisms.
×