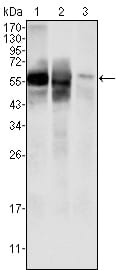
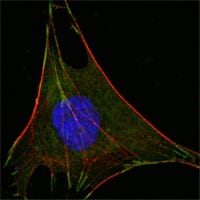
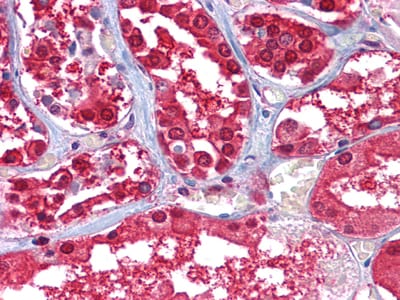
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AMF; NLK; PGI; PHI; GNPI; SA-36; GPI |
| Entrez GeneID | 2821 |
| clone | 1B7D7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 63kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human GPI expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase(GPI)抗体相关的研究文献摘要简述:
---
1. **文献名称**:Autoantibodies to glucose-6-phosphate isomerase in rheumatoid arthritis
**作者**:Schaller M et al.
**摘要**:该研究发现类风湿关节炎(RA)患者血清中存在针对GPI的自身抗体,并通过小鼠模型证实抗GPI抗体可诱导关节炎,提示GPI可能是RA的关键自身抗原之一。
---
2. **文献名称**:Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase promotes tumor metastasis through enhancing the function of cell surface ATP synthase
**作者**:Sun L et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示GPI在肿瘤细胞表面通过调控ATP合酶活性促进转移,抗GPI抗体可阻断此通路并抑制小鼠模型中癌细胞的侵袭和转移能力。
---
3. **文献名称**:Anti-glucose-6-phosphate isomerase antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
**作者**:Choi MY et al.
**摘要**:报道系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者中存在抗GPI抗体,其水平与疾病活动性相关,提示GPI抗体可能作为SLE的新型生物标志物及潜在治疗靶点。
---
如需更多文献或具体研究方向(如实验方法学),可进一步补充说明。
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI), also known as phosphoglucose isomerase or neuroleukin, is a multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the reversible isomerization of glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate during glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. Beyond its metabolic role, GPI exhibits cytokine-like activity, influencing cell growth, differentiation, and immune responses. Antibodies targeting GPI have gained attention due to their association with autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), anti-GPI antibodies are detected in synovial fluid and serum, contributing to joint inflammation through immune complex deposition and complement activation. Their presence correlates with disease severity in animal models, suggesting a pathogenic role.
Anti-GPI antibodies are also implicated in other conditions, including certain cancers and neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, though these links remain less defined. Research highlights GPI’s dual nature as both an enzyme and an autoantigen, with epitope-specific antibodies potentially driving tissue damage. However, clinical utility as a biomarker is debated due to variability in detection methods and inconsistent correlations across patient cohorts. Standardization of assays and deeper mechanistic insights into GPI-antibody interactions are needed to clarify their diagnostic and therapeutic relevance. Overall, GPI antibodies represent a fascinating intersection of metabolism and autoimmunity, warranting further exploration.
×