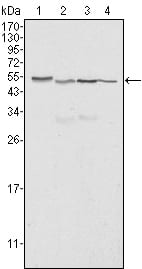
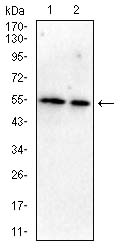
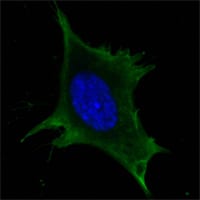
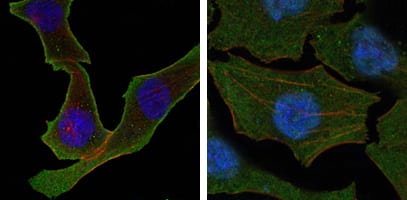
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| IHC | 1/100 - 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| ICC | 1/50 - 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
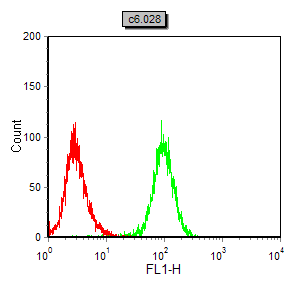
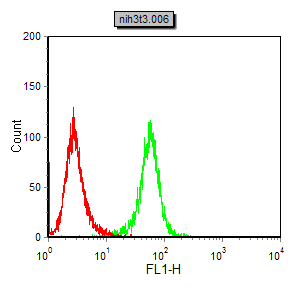
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| Aliases | RO; CRT; SSA; cC1qR; FLJ26680; CALR |
| Entrez GeneID | 811 |
| clone | 1G6A7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 48kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide corresponding to aa (EEEDVPGQAKDELC) of human Calreticulin, conjugated to KLH. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与Calreticulin抗体相关的代表性文献摘要:
1. **文献名称**:Calreticulin mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms
**作者**:Klampfl T, et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次发现骨髓增殖性肿瘤(MPN)患者中CALR基因的体细胞突变,导致异常Calreticulin蛋白表达,并揭示了其与JAK2阴性患者的血栓形成和自身免疫反应相关。
2. **文献名称**:Autoantibodies against calreticulin in systemic autoimmune diseases
**作者**:Nishiura H, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)和类风湿关节炎(RA)患者血清中存在抗Calreticulin自身抗体,提示Calreticulin可能作为自身抗原参与自身免疫疾病的病理过程。
3. **文献名称**:Surface-exposed calreticulin in the immunogenic apoptosis
**作者**:Obeid M, et al.
**摘要**:阐明Calreticulin在细胞应激时易位至细胞表面,成为“eat me”信号,促进吞噬细胞清除凋亡细胞,这一机制在癌症免疫治疗(如化疗/放疗诱导的免疫原性细胞死亡)中起关键作用。
(注:以上内容为基于领域知识的概括,实际文献需通过PubMed等数据库检索具体信息)
Calreticulin (CALR) is a multifunctional, calcium-binding chaperone protein primarily located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where it plays a key role in calcium homeostasis, protein folding, and quality control. Antibodies targeting calreticulin have gained attention in both research and clinical contexts. In autoimmune diseases, anti-calreticulin antibodies are detected in conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis, potentially linked to molecular mimicry or aberrant exposure of CALR during cell stress or apoptosis.
In hematology, somatic mutations in the *CALR* gene (e.g., exon 9 deletions/insertions) are hallmark drivers of certain myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), such as essential thrombocythemia and primary myelofibrosis. These mutations alter CALR’s structure, leading to pathologic activation of thrombopoietin receptors. While CALR mutations themselves are not direct targets of antibodies, anti-CALR antibodies may arise as part of autoimmune responses in MPN patients.
Structurally, CALR has three domains: N-terminal, proline-rich, and C-terminal, each with distinct functions. Antibodies targeting specific domains help study CALR’s roles in immunogenic cell death, where surface-exposed CALR acts as an “eat-me” signal for phagocytes. Clinically, anti-CALR antibodies are explored as diagnostic tools or biomarkers, though their pathogenic significance remains under investigation. Research also focuses on CALR’s immunomodulatory roles in cancer therapy, leveraging its ability to enhance antigen presentation and antitumor immunity.
×