| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
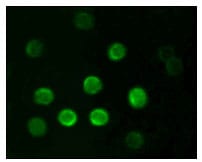
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
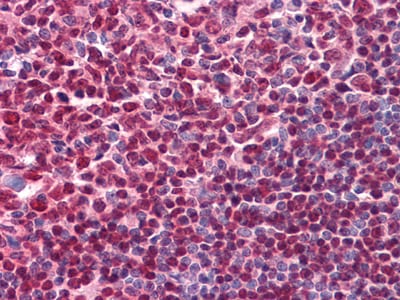
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B1; S7; Bp35; CD20; MS4A2; LEU-16; MGC3969; MS4A1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 931 |
| clone | 3E9D3C1G3 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide corresponding to aa (EPANPSEKNSPSTQY) of human CD20,conjugated to KLH. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD20抗体的经典文献示例:
---
1. **文献名称**:Rituximab chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy for relapsed indolent lymphoma: half of patients respond to a four-dose treatment program
**作者**:McLaughlin P, et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了利妥昔单抗(抗CD20单抗)在复发性惰性淋巴瘤中的疗效,显示约50%患者接受4次治疗后出现客观缓解,奠定了其在血液肿瘤治疗中的基础。
---
2. **文献名称**:Obinutuzumab (GA101) in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: final data from the phase 1/2 GAUGUIN study
**作者**:Sehn LH, et al.
**摘要**:研究评估了第二代CD20抗体Obinutuzumab在复发/难治慢性淋巴细胞白血病中的效果,显示其较一代抗体更强的抗体依赖细胞毒作用(ADCC)和临床应答率。
---
3. **文献名称**:Ofatumumab versus rituximab in relapsed CD20+ follicular lymphoma: distinct mechanisms may lead to enhanced efficacy
**作者**:Cartron G, et al.
**摘要**:比较了Ofatumumab与利妥昔单抗在滤泡性淋巴瘤中的差异,指出Ofatumumab因更紧密的CD20结合和补体依赖性细胞毒作用(CDC)可能具有更优疗效。
---
4. **文献名称**:Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies: historical and future perspectives
**作者**:Lim SH, et al.
**摘要**:综述性文献,系统总结了CD20抗体的发展历程、作用机制(如抗原调变、直接诱导凋亡)及在肿瘤和自身免疫病(如多发性硬化症)中的临床应用进展。
---
*注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时需核对具体来源及准确性。如需正式引用,建议通过PubMed等数据库确认最新研究。*
CD20 is a transmembrane protein expressed on the surface of B cells, from pre-B to mature stages, but absent on plasma cells. Discovered in 1980. it became a pivotal therapeutic target due to its role in B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases. The restricted expression profile minimizes off-target effects, making it ideal for antibody-based therapies.
The first anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, rituximab, was approved in 1997 for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, revolutionizing cancer treatment as one of the earliest successful monoclonal antibody therapies. It works through multiple mechanisms: complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP), and direct induction of apoptosis. Later-generation anti-CD20 antibodies (e.g., ofatumumab, obinutuzumab) were engineered to enhance efficacy by modifying Fc regions for improved immune cell engagement or altering epitope binding.
Anti-CD20 therapies now treat diverse conditions, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. However, challenges persist, such as variable patient responses, CD20 downregulation in resistant tumors, and infusion-related reactions. Research continues to optimize dosing, develop bispecific antibodies (e.g., CD20xCD3 T-cell engagers), and explore combination therapies with checkpoint inhibitors. Recent advances also highlight their role in modulating B-cell-driven immune dysregulation beyond oncology, expanding therapeutic potential in autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases.
×