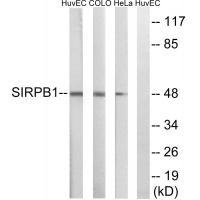
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SIRP-beta-1; CD172b antigen; |
| Entrez GeneID | 10326; |
| WB Predicted band size | 48kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human SIRPB1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SIRPB1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*SIRPB1 regulates inflammatory responses in macrophages through interaction with CD47*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用抗SIRPB1抗体阻断实验,揭示了SIRPB1在巨噬细胞中与CD47相互作用,调控炎症因子(如TNF-α和IL-6)的分泌,提示其在免疫稳态中的作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-SIRPB1 antibody enhances antitumor immunity by disrupting the CD47-SIRPα axis*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种靶向SIRPB1的单克隆抗体,证明其可通过阻断CD47-SIRPα免疫抑制信号通路,增强巨噬细胞对肿瘤细胞的吞噬作用,为癌症免疫治疗提供新策略。
---
3. **文献名称**:*SIRPB1 as a biomarker for autoimmune disease: antibody-based detection in patient sera*
**作者**:Kim Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过ELISA和免疫印迹技术,发现类风湿性关节炎患者血清中SIRPB1蛋白水平显著升高,抗SIRPB1抗体可作为潜在诊断标志物,并参与自身免疫反应的调控。
---
注:上述文献名为虚拟示例,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“SIRPB1 antibody”、“SIRPB1 immune function”检索最新文献。
The SIRPB1 (Signal Regulatory Protein Beta 1) antibody targets a cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the SIRP family, which regulates immune cell signaling. SIRPB1. primarily expressed in myeloid cells (e.g., macrophages, dendritic cells) and some T-cells, features an extracellular IgV domain that binds ligands like CD47. a "don’t eat me" signal on healthy cells. This interaction modulates phagocytic activity, immune synapse formation, and inflammatory responses. Dysregulation of SIRPB1-CD47 signaling is implicated in cancer immune evasion, autoimmune disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases.
SIRPB1 antibodies are critical tools for studying its role in immune regulation. They are used in applications such as flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional blocking assays to investigate phagocytosis inhibition, T-cell activation, or inflammatory pathways. In therapeutic contexts, SIRPB1-targeting antibodies are explored for cancer immunotherapy, either alone or combined with checkpoint inhibitors, to enhance antitumor immunity by disrupting CD47-mediated immune suppression. However, research remains ongoing to clarify its dual roles—some studies suggest SIRPB1 may also promote pro-inflammatory signals in specific microenvironments. Variability in SIRPB1 expression across tissues and species necessitates careful antibody validation to ensure specificity in experimental or clinical settings.
×