
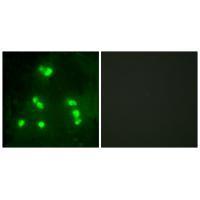
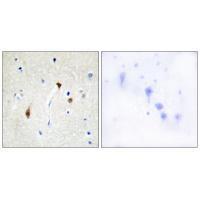
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Protein hairless; HR; HAIR; |
| Entrez GeneID | 55806; |
| WB Predicted band size | 130kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human HAIR. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于抗胰岛素受体抗体(HAIR抗体,常见于HAIR-AN综合征)的3篇代表性文献,简要整理如下:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Clinical Course of the Syndrome of Autoantibodies to the Insulin Receptor"*
**作者**:Arioglu E, et al.
**摘要**:分析了30例抗胰岛素受体抗体阳性患者的临床特征,发现其与严重胰岛素抵抗、高雄激素血症及黑棘皮症相关,探讨抗体阻断或激活受体功能的双重机制。
2. **文献名称**:*"Autoantibodies to the Insulin Receptor in Human Insulin Resistance Syndromes"*
**作者**:Taylor SI, et al.
**摘要**:系统阐述抗胰岛素受体抗体在B型胰岛素抵抗中的作用,发现抗体可通过干扰胰岛素信号通路导致糖代谢异常,部分患者合并自身免疫性疾病。
3. **文献名称**:*"A Novel Assay for Insulin Receptor Autoantibodies"*
**作者**:Kawasaki E, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种基于细胞实验的检测方法,证实抗胰岛素受体抗体在不同疾病中的异质性,为临床诊断提供高灵敏度检测手段。
---
如需更具体的研究方向或近年文献,可进一步补充说明。
HAIR antibodies, or anti-hair follicle antibodies, are autoantibodies targeting components of hair follicles, implicated in autoimmune hair loss disorders. First identified in studies on alopecia areata (AA), these antibodies are thought to contribute to immune-mediated attacks on hair follicle structures, leading to hair loss. Research suggests they may recognize antigens such as trichohyalin, keratinocytes, or melanocyte-related proteins within the follicle.
The presence of HAIR antibodies is often detected via immunofluorescence or ELISA, showing higher titers in active AA cases. Their role remains debated: while some studies propose a direct pathogenic role, others consider them secondary markers of follicular damage. Genetic predisposition, environmental triggers (e.g., stress, infections), and immune dysregulation involving T-cells and cytokines (e.g., IFN-γ) likely interact in HAIR antibody formation.
HAIR antibodies are also explored in scarring alopecias (e.g., lichen planopilaris) and systemic autoimmune conditions (e.g., lupus), broadening their clinical relevance. However, standardized detection methods and diagnostic specificity remain challenges. Recent advances highlight potential therapeutic targets, such as JAK inhibitors, which modulate immune pathways linked to HAIR antibody activity. Further research is needed to clarify their precise mechanisms and optimize biomarker utility in managing hair loss disorders.
×