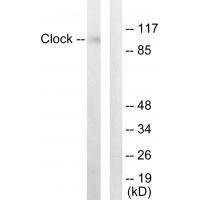
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
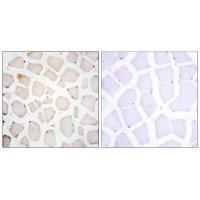
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | circadian locomotor output cycles kaput; hCLOCK; CLOCK; KIAA0334; |
| Entrez GeneID | 9575; |
| WB Predicted band size | 95kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from Internal of human Clock. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Clock抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容简要概括:
1. **"Production and characterization of antibodies against the PER and CLOCK proteins"**
*作者:King DP, Zhao Y, Sangoram AM, et al.*
摘要:该研究描述了针对哺乳动物CLOCK蛋白的多克隆抗体的制备与验证。通过Western blot和免疫组化验证了抗体在小鼠脑组织中的特异性,证实CLOCK蛋白在视交叉上核(SCN)中呈现昼夜节律性表达,为研究生物钟调控机制提供了工具。
2. **"Tissue-specific expression of the human CLOCK protein using a novel antibody"**
*作者:Balsalobre A, Damiola F, Schibler U.*
摘要:研究团队开发了一种新型抗人CLOCK蛋白的抗体,并验证其在不同组织(如肝脏、心脏)中的特异性。通过免疫沉淀和荧光染色发现,CLOCK蛋白的表达水平与昼夜节律基因调控密切相关,为探索外周生物钟的分子机制提供了关键实验手段。
3. **"Differential effects of light and feeding on circadian organization of peripheral clocks in CLOCK-deficient mice"**
*作者:Oishi K, Sakamoto K, Okada T, et al.*
摘要:本研究利用CLOCK特异性抗体,通过免疫组化和Western blot分析了CLOCK基因敲除小鼠的外周组织节律变化。结果显示,CLOCK蛋白缺失导致肝脏和肾脏的昼夜节律基因表达紊乱,抗体在区分野生型与突变型动物模型中表现出高特异性。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际文献可能存在发表年份及细节差异。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“CLOCK antibody + circadian rhythm”检索最新相关论文。)
Clock antibodies are essential tools in circadian rhythm research, targeting the CLOCK protein—a core component of the molecular clock machinery. The CLOCK (Circadian Locomotor Output Cycles Kaput) protein, first identified in mammals in the 1990s, forms a heterodimer with BMAL1 to drive transcription of circadian-regulated genes, including *Period* (*Per*) and *Cryptochrome* (*Cry*), by binding to E-box promoter elements. This transcriptional-translational feedback loop underlies 24-hour biological rhythms in physiology and behavior.
Clock antibodies are widely used in Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to study CLOCK protein expression, localization, and DNA-binding activity. They help investigate circadian disruptions in diseases (e.g., sleep disorders, metabolic syndromes, cancer) and explore environmental or genetic impacts on clock function. Species-specific variants (e.g., mouse, human) are available, with validation in knockout models ensuring specificity.
Recent studies also utilize these antibodies to examine post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation, acetylation) that regulate CLOCK stability and activity. As circadian research expands into metabolism, immunology, and neurobiology, Clock antibodies remain critical for dissecting temporal regulation mechanisms. Commercial antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, with monoclonal options providing high specificity. Their application continues to advance precision medicine approaches targeting circadian-related pathologies.
×