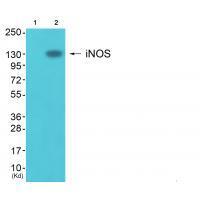
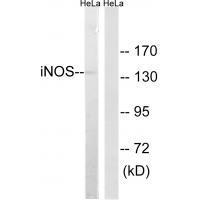
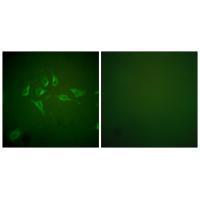
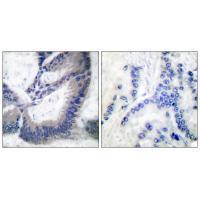
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NITRIC OXIDE SYNTHASE; INDUCIBLE; NITRIC OXIDE SYNTHASE; MACROPHAGE; NOS2A |
| Entrez GeneID | 4843; |
| WB Predicted band size | 130kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human iNOS. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于iNOS抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖不同研究领域:
1. **"Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in tumor-associated macrophages"**
- **作者**: Qian B.Z. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究通过免疫组化及Western blot使用iNOS抗体,发现肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAMs)中iNOS高表达与肿瘤血管生成和转移相关,提示iNOS可能作为癌症治疗的潜在靶点。
2. **"iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production in infectious disease pathogenesis"**
- **作者**: Nathan C. et al.
- **摘要**: 利用iNOS特异性抗体检测小鼠感染模型中的酶活性,证实iNOS在宿主防御细菌和寄生虫感染中的关键作用,并揭示其过度表达可能导致组织损伤。
3. **"Selective inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase exacerbates Alzheimer's disease pathology"**
- **作者**: Colton C.A. et al.
- **摘要**: 通过免疫荧光染色结合iNOS抗体,研究发现iNOS在阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型的小胶质细胞中显著上调,抑制iNOS可能加重淀粉样斑块沉积,提示其双刃剑效应。
4. **"Pharmacological modulation of iNOS expression in inflammatory bowel disease"**
- **作者**: Kolios G. et al.
- **摘要**: 在结肠炎模型中,采用iNOS抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫组化分析,发现特定抗炎药物通过下调iNOS减轻肠道炎症,为IBD治疗提供新方向。
以上文献展示了iNOS抗体在癌症、感染、神经疾病及炎症研究中的应用,均聚焦于iNOS表达调控及其病理生理意义。
Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), also known as NOS2. is an enzyme that catalyzes the production of nitric oxide (NO) from L-arginine. Unlike constitutive NOS isoforms (eNOS and nNOS), iNOS is not typically expressed under normal physiological conditions but is induced in response to inflammatory stimuli, such as cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β) or microbial products. It plays a critical role in immune defense by generating NO, which exhibits antimicrobial, antiviral, and antitumor properties. However, excessive or prolonged iNOS activation is linked to chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and pathologies like sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, and neurodegenerative diseases.
iNOS antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying iNOS expression in research. These antibodies enable the study of iNOS regulation in immune cells (e.g., macrophages), inflamed tissues, or cancer microenvironments. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to explore iNOS involvement in disease mechanisms or therapeutic responses. Commercial iNOS antibodies are often validated for specificity against conserved epitopes, though cross-reactivity with other NOS isoforms requires careful controls. Research utilizing these antibodies has advanced understanding of dual roles of iNOS-derived NO—both protective and harmful—depending on context, offering insights into targeted therapies for inflammatory and immune-related disorders.
×