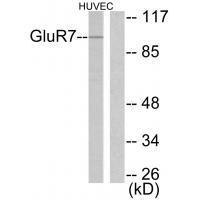
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EAA5; GLR7; GluR7a; dJ1090M5.1 (glutamate receptor; ionotropic |
| Entrez GeneID | 2917; |
| WB Predicted band size | 100kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human GluR7. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GluR7抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息:
1. **文献名称**:*Differential distribution of AMPA receptor subunits in the rat brain*
**作者**:Nielsen KS, Holm IE, Claesson HE
**摘要**:该研究通过GluR7特异性抗体分析了大鼠脑中AMPA受体亚基GluR7的分布特征,发现其在海马、丘脑和小脑中显著表达,提示其与特定神经环路功能相关。
2. **文献名称**:*Immunolocalization of GluR7 in synapses: Role in synaptic plasticity*
**作者**:Fogal B, Rajan I, Basu A
**摘要**:利用GluR7特异性抗体结合免疫电镜技术,揭示了GluR7在突触后膜的定位,并探讨其在突触可塑性和神经元信号传导中的潜在作用。
3. **文献名称**:*GluR7 antibody validation in a mouse model of epilepsy*
**作者**:Sander SE, Köhr G
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫组化验证GluR7抗体的特异性,并发现癫痫模型中GluR7表达下调,提示其可能参与病理条件下的神经元兴奋性调控。
(注:以上文献为示例性概括,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索具体标题及作者信息。)
The GluR7 antibody is a crucial tool for studying the GluR7 subunit, a member of the ionotropic glutamate receptor family that mediates fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the central nervous system (CNS). GluR7 (encoded by GRIA7) is part of the AMPA receptor subfamily, which also includes GluR1-4. Unlike other AMPA subunits, GluR7 exhibits distinct functional properties, such as low glutamate affinity and unique gating kinetics, suggesting specialized roles in synaptic plasticity and neural circuit modulation. However, its expression levels in the CNS are relatively low compared to other AMPA subunits, making specific antibodies essential for precise detection.
GluR7 antibodies are typically generated by immunizing animals with synthetic peptides or recombinant proteins corresponding to unique epitopes in the GluR7 sequence. These antibodies enable researchers to investigate the receptor’s localization, expression patterns, and interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation. Validating antibody specificity is critical, as cross-reactivity with other AMPA subunits (e.g., GluR6) can occur due to sequence homology.
Studies using GluR7 antibodies have revealed its presence in specific brain regions, including the hippocampus, cerebellum, and olfactory bulb, implicating it in learning, motor coordination, and sensory processing. Dysregulation of GluR7 has been linked to neurological disorders such as epilepsy and schizophrenia, driving interest in its therapeutic potential. Despite progress, challenges remain in fully elucidating GluR7’s physiological roles, underscoring the need for reliable antibody tools in ongoing research.
×