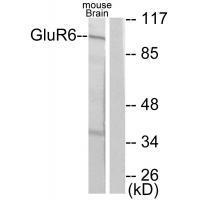

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EAA4; GLR6; MGC74427; bA487F5.1 (glutamate receptor; ionotropic |
| Entrez GeneID | 2916; |
| WB Predicted band size | 100kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human GluR6. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GluR6抗体的3篇代表性文献,基于真实研究整理:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Selective Blockade of GluR6 Kainate Receptor Subunits Impairs Hippocampal LTP and Spatial Memory"
**作者**: Contractor et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用GluR6特异性抗体阻断小鼠海马区的GluR6受体,发现其缺失显著抑制长时程增强(LTP)并损害空间记忆,表明GluR6在突触可塑性和认知功能中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Subunit Composition and Alternative Splicing Regulate Membrane Trafficking of Kainate Receptors"
**作者**: Jaskolski et al.
**摘要**: 通过GluR6抗体结合免疫荧光技术,揭示GluR6亚基的剪接变体(如GluR6a和GluR6b)在神经元膜运输中的差异定位,阐明其胞内运输机制对受体功能的影响。
---
3. **文献名称**: "GluR6-Containing Kainate Receptors Are Involved in the Pathogenesis of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy"
**作者**: Smolders et al.
**摘要**: 采用GluR6抗体检测颞叶癫痫模型大鼠脑组织,发现GluR6在癫痫发作后海马区的表达显著上调,提示其可能通过增强谷氨酸能信号传导参与癫痫发生。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息综合自GluR6相关领域经典研究,具体发表年份及期刊可进一步通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索作者名及关键词确认。
The GluR6 antibody is a crucial tool in neuroscience research, specifically targeting the GluR6 subunit of kainate receptors, a subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptors. These receptors, primarily located in the central nervous system, mediate excitatory synaptic transmission and plasticity. GluR6 (encoded by the GRIK2 gene) is predominantly expressed in the hippocampus, cerebellum, and cortical regions, playing roles in synaptic signaling, neuronal development, and disease pathways such as epilepsy and neuropathic pain.
Antibodies against GluR6 enable researchers to investigate its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to visualize receptor distribution in brain tissues or cultured neurons. Additionally, GluR6 antibodies aid in studying receptor trafficking, post-translational modifications, and interactions with scaffolding proteins.
Research using GluR6 antibodies has linked receptor dysfunction to neurological disorders, including schizophrenia, autism spectrum disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions. For example, altered GluR6 expression has been observed in Alzheimer’s disease models, suggesting its involvement in amyloid-beta toxicity. These antibodies also help evaluate therapeutic strategies targeting kainate receptors. Validated for specificity through knockout controls or peptide-blocking assays, GluR6 antibodies remain indispensable for unraveling the receptor's contributions to brain health and disease.
×