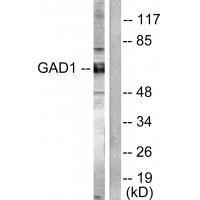
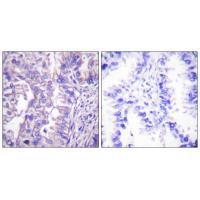
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Glutamate decarboxylase 2; EC 4.1.1.15; Glutamate decarboxylase 65 kDa isoform; GAD-65; 65 kDa glutamic acid decarboxylase |
| Entrez GeneID | 2571;2572; |
| WB Predicted band size | 65kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human GAD1/GAD2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GAD1/2抗体的3-4篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**: *Identification of the 64K autoantigen in type 1 diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase*
**作者**: Baekkeskov S, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究首次证实1型糖尿病中的64K自身抗原为GAD65(GAD2),揭示了其作为疾病标志物的作用,为后续自身免疫糖尿病诊断提供了重要依据。
2. **文献名称**: *Two genes encode distinct glutamate decarboxylases*
**作者**: Erlander MG, et al.
**摘要**: 文章克隆并鉴定了GAD67(GAD1)和GAD65(GAD2)两种亚型,阐明了二者在组织分布和功能上的差异,并开发了特异性抗体用于区分两者。
3. **文献名称**: *Stiff-person syndrome: quantification, specificity, and intrathecal synthesis of GAD65 antibodies*
**作者**: Dalakas MC, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现僵人综合征患者脑脊液中GAD65抗体水平显著升高,提示抗体可能通过干扰GABA能信号通路导致中枢神经系统过度兴奋。
4. **文献名称**: *GAD antibody-associated neurological disorders: Progress and emerging challenges*
**作者**: Manto MU, et al.
**摘要**: 综述总结了抗GAD抗体与多种神经系统疾病(如小脑共济失调、癫痫)的关联,探讨了抗体在致病机制中的作用及临床检测意义。
这些文献涵盖了GAD抗体在自身免疫疾病诊断、亚型特异性研究及神经疾病机制中的关键作用。
**Background of GAD1/2 Antibodies**
Glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of glutamate to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Two isoforms, GAD67 (encoded by *GAD1*) and GAD65 (encoded by *GAD2*), are expressed in mammals. GAD67 is constitutively active and primarily localized to neuronal cell bodies, while GAD65 is transiently activated and associated with synaptic vesicles, playing a key role in GABA synthesis for rapid neurotransmission.
Antibodies targeting GAD1/2 are widely used in research to study GABAergic system dynamics, neuronal development, and disorders like epilepsy, schizophrenia, and Parkinson’s disease. In clinical contexts, autoantibodies against GAD65 (not GAD67) are biomarkers for autoimmune conditions, notably type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and stiff-person syndrome (SPS). These autoantibodies arise from immune-mediated targeting of pancreatic beta cells or CNS neurons, leading to functional impairment.
Research-grade GAD1/2 antibodies are critical tools for immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, or ELISA to map GABAergic pathways or quantify expression changes in disease models. Their specificity and validation (e.g., knockout validation) are essential to avoid cross-reactivity, given the high sequence homology between GAD isoforms. Clinically, detecting GAD65 autoantibodies aids in diagnosing and monitoring autoimmune disorders, reflecting both diagnostic challenges and therapeutic opportunities.
×