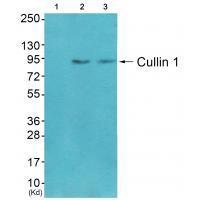
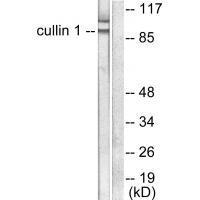
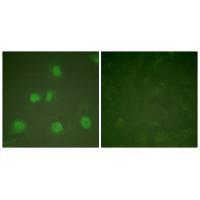
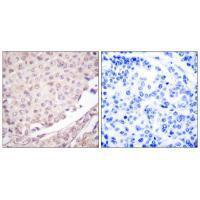
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cullin-1; CUL-1; |
| Entrez GeneID | 8454; |
| WB Predicted band size | 90kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human Cullin 1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Cullin 1抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Cullin 1 is a potential biomarker for colorectal cancer progression*
**作者**:Hao, B., et al. (2017)
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫组化及Western blot分析,发现Cullin 1在结直肠癌组织中显著高表达,并与肿瘤分期和转移相关。研究利用特异性Cullin 1抗体验证其作为预后标志物的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Neddylation of Cullin 1 regulates its interaction with Skp1 in the SCF ubiquitin ligase complex*
**作者**:Skaar, J.R., et al. (2013)
**摘要**:本文探讨了Cullin 1的neddylation修饰对其与Skp1结合的影响。通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和Western blot实验(使用Cullin 1抗体),发现neddylation缺失会破坏SCF复合体稳定性,抑制泛素化功能。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural basis for Cul1 protein assembly with the F-box protein Skp2*
**作者**:Zheng, N., et al. (2002)
**摘要**:该研究解析了Cullin 1与Skp2结合的晶体结构,揭示其介导底物识别的机制。实验中利用Cullin 1抗体验证重组蛋白的相互作用,为SCF复合体功能提供了结构生物学依据。
---
以上文献涵盖了Cullin 1在疾病关联、翻译后修饰及结构功能中的研究,均涉及抗体的实验应用(如Western blot、免疫组化或Co-IP)。如需扩展,可进一步检索近年关于Cullin家族蛋白调控机制的研究。
Cullin 1 (CUL1) is a core component of the Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase (CRL) complexes, which regulate protein ubiquitination and degradation via the proteasome. As a scaffold protein, CUL1 assembles with Rbx1 (RING-box protein 1) at its C-terminus and adaptor proteins (e.g., Skp1) at its N-terminus to form SCF (Skp1-Cul1-F-box) E3 ligases. These complexes target specific substrates—such as cell cycle regulators (e.g., cyclins) and signaling molecules—for degradation, playing critical roles in cell cycle progression, DNA repair, and transcriptional regulation. Dysregulation of CUL1 is linked to cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, and developmental defects.
CUL1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions in biological systems. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to investigate CUL1’s involvement in disease mechanisms or drug responses. These antibodies are often raised against epitopes in conserved regions (e.g., N-terminal or C-terminal domains) and validated for specificity across species (human, mouse, rat). Researchers also employ CUL1 antibodies to explore CRL complex dynamics, substrate recognition, and the impact of post-translational modifications (e.g., neddylation) on ligase activity. Their applications extend to screening therapeutic agents targeting ubiquitin-proteasome pathways or biomarker discovery in oncology.
×