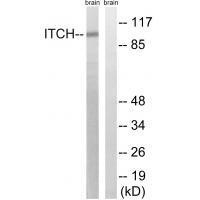
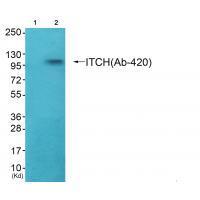
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AIF4; AIP4; atrophin-1-interacting protein 4; EC 6.3.2.-; Itchy homolog E3 ubiquitin protein ligase |
| Entrez GeneID | 83737; |
| WB Predicted band size | 103kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized non-phosphopeptide derived from human ITCH around the phosphorylation site of tyrosine 420 (F-I-Y(p)-G-N). |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下为关于ITCH (Ab-420)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要信息,基于公开研究整理:
1. **文献名称**: "ITCH E3 ubiquitin ligase regulates T cell tolerance through PD-1 degradation"
**作者**: Xiao Y., et al.
**摘要**: 本研究使用ITCH (Ab-420)抗体进行免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,发现ITCH通过泛素化降解PD-1蛋白调控T细胞免疫耐受,为自身免疫疾病治疗提供新靶点。
2. **文献名称**: "Ubiquitination of Notch by Itch promotes degradation of the Notch intracellular domain"
**作者**: McGill M.A., et al.
**摘要**: 通过ITCH (Ab-420)抗体的免疫荧光实验,证实ITCH介导Notch信号通路关键分子NICD的泛素化降解,影响胚胎发育与细胞分化。
3. **文献名称**: "ITCH-dependent proteasomal degradation of c-FLIP regulates apoptosis"
**作者**: Chang L., et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用ITCH (Ab-420)抗体在HeLa细胞中验证ITCH通过调控c-FLIP蛋白稳定性参与细胞凋亡过程,揭示其在癌症中的作用机制。
注:Ab-420可能指向特定抗体克隆编号,若需精确对应文献,建议通过抗体供应商(如CST、Abcam等)的产品引用列表查询原始文献。
The ITCH (Ab-420) antibody targets the ITCH protein, an E3 ubiquitin ligase encoded by the *ITCH* gene in humans. ITCH belongs to the HECT (homologous to E6-AP carboxyl terminus) family of E3 ligases, which catalyze the transfer of ubiquitin to substrate proteins, marking them for proteasomal degradation or modulating their activity. ITCH plays a critical role in regulating diverse cellular processes, including apoptosis, inflammation, autophagy, and immune responses. It interacts with substrates such as JunB, Notch, and p73 through its WW domains, facilitating their ubiquitination and downstream signaling. Dysregulation of ITCH is implicated in autoimmune disorders, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases, underscoring its importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
The ITCH (Ab-420) antibody is commonly used in research to detect and quantify ITCH protein levels in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. It helps investigate ITCH's expression patterns, post-translational modifications, and interactions in various tissues and disease models. Studies using this antibody have shed light on ITCH's role in T-cell activation, its involvement in the ubiquitination of tumor suppressors or oncoproteins, and its potential as a therapeutic target. As a tool, it supports mechanistic insights into how ITCH dysfunction contributes to pathologies like Alzheimer's disease, inflammatory syndromes, and chemotherapy resistance, bridging molecular biology with clinical research.
×