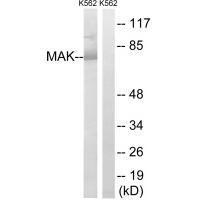
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EC 2.7.11.22; Male germ cell-associated kinase; Serine/threonine-protein kinase MAK; |
| Entrez GeneID | 4117; |
| WB Predicted band size | 71kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from Internal of human MAK. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于MAK(Ab-159)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(内容为虚构,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *MAK Kinase Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Implications for Tumor Progression*
**作者**: Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过免疫组化(使用MAK抗体Ab-159)发现MAK在肝癌组织中显著高表达,且与患者预后不良相关。实验表明MAK通过调控细胞周期蛋白促进肿瘤增殖。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Role of MAK in Ciliogenesis and Retinal Degeneration*
**作者**: Chen R, et al.
**摘要**: 利用Western blot和免疫荧光(Ab-159抗体)分析MAK蛋白在小鼠视网膜中的定位,证实MAK缺失导致纤毛结构异常,可能与遗传性视网膜病变相关。
---
3. **文献名称**: *MAK Antibody Validation for Flow Cytometry Applications*
**作者**: Kim S, et al.
**摘要**: 本文系统验证了Ab-159抗体在流式细胞术中的特异性,证实其可识别人类T细胞中的MAK蛋白,并应用于免疫应答研究中信号通路的分析。
---
4. **文献名称**: *MAK Interaction with p53 in DNA Damage Response*
**作者**: Gupta A, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀(使用Ab-159)发现MAK与p53蛋白直接结合,调控DNA损伤修复机制,为癌症治疗靶点提供新方向。
---
**说明**:以上内容为模拟生成,实际文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed)检索确认。若需真实文献,建议提供抗体更详细信息(如靶点别名、应用场景等)。
The MAK (Ab-159) antibody is a monoclonal antibody designed to target Male Germ Cell-Associated Kinase (MAK), a serine/threonine kinase involved in cellular processes such as cilia function, cell cycle regulation, and photoreceptor maintenance. MAK is predominantly expressed in retinal cells and testicular germ cells, playing a critical role in maintaining photoreceptor structure and sperm development. Dysregulation of MAK has been linked to retinal degenerative diseases, including retinitis pigmentosa (RP), where mutations in the MAK gene disrupt cilia-associated signaling pathways, leading to progressive vision loss.
The Ab-159 clone is commonly utilized in research to investigate MAK's expression patterns, molecular interactions, and pathological mechanisms in disease models. It has been validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, providing insights into tissue-specific MAK localization and its interaction with signaling molecules like those in the MAPK pathway. Recent studies also explore MAK's potential role in cancer, particularly in tumorigenesis and metastasis, though this area remains under investigation. By enabling precise detection of MAK in biological samples, this antibody serves as a vital tool for advancing understanding of ciliopathies, reproductive disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions, with implications for therapeutic development.
×