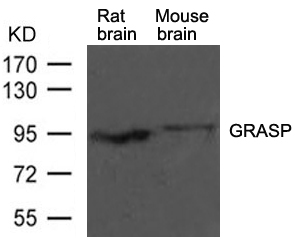
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Gripap; Grasp; GRIP1-associated protein |
| Entrez GeneID | 116493; |
| WB Predicted band size | 95kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around aa. 814-818(Q-E-I-V-R ) derived from Rat GRASP. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GRASP抗体的3篇参考文献概览:
1. **文献名称**: *GRASP55 regulates Golgi morphology and autophagy in mammalian cells*
**作者**: Zong M. et al.
**摘要**: 研究聚焦GRASP55蛋白在哺乳动物细胞中调控高尔基体形态及自噬过程的作用,通过抗体阻断实验证实其参与细胞器结构与自噬小体形成的分子机制。
2. **文献名称**: *Antibody-based detection of GRASP65 reveals its role in Golgi stack formation*
**作者**: Barr F.A. et al.
**摘要**: 开发特异性抗GRASP65抗体,揭示该蛋白在高尔基体堆叠形成中的关键功能,为研究分泌途径与细胞内膜运输提供工具支持。
3. **文献名称**: *GRASP proteins are required for ER-to-Golgi transport during C. elegans development*
**作者**: Liu Y. et al.
**摘要**: 利用GRASP抗体进行免疫定位,发现线虫发育过程中GRASP家族蛋白对ER到高尔基体的囊泡运输不可或缺,拓展了对该蛋白在模式生物中的功能认知。
注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用请以具体研究内容匹配真实文献。
GRASP antibodies are essential tools in studying the Golgi Reassembly and Stacking Protein (GRASP) family, primarily GRASP55 (GORASP1) and GRASP65 (GORASP2), which play critical roles in Golgi apparatus structure and function. These proteins facilitate the formation and maintenance of Golgi stacks by mediating membrane tethering and cisternal stacking. Beyond their structural role, GRASP proteins are involved in unconventional protein secretion, cell cycle regulation, and stress responses, making them significant in cellular homeostasis and disease contexts.
GRASP antibodies enable researchers to detect and localize these proteins via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. They help investigate GRASP’s interactions with other Golgi components, its phosphorylation states, and its dynamic behavior during mitosis or cellular stress. Dysregulation of GRASP proteins has been linked to pathologies such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and infectious diseases, where Golgi dysfunction contributes to pathogenesis.
These antibodies are pivotal in exploring GRASP’s dual roles in structural organization and signaling, offering insights into cellular adaptation mechanisms. Their application spans basic research on organelle biology to translational studies targeting GRASP-related diseases, underscoring their versatility in both mechanistic and clinical investigations.
×