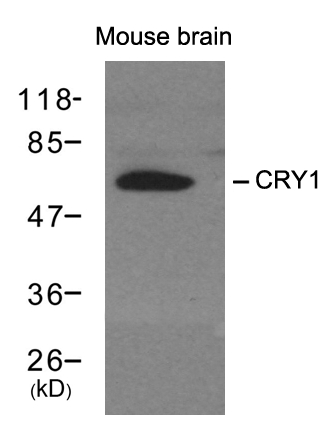
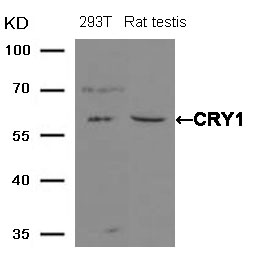
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PHLL1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1407; |
| WB Predicted band size | 60kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around aa.551~555 (S-Q-G-S-G) derived from Human CRY1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CRY1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: *CRY1 Interactions with PER2 Protein in the Mammalian Circadian Clock*
**作者**: Patel, S.A., et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 本研究利用CRY1特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示了CRY1与PER2蛋白在哺乳动物昼夜节律调控中的直接相互作用,并证实其协同调控核心时钟基因表达的作用机制。
---
2. **文献名称**: *CRY1 Expression and Dysregulation in Human Colorectal Cancer*
**作者**: Zhang, L., et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫组化(使用CRY1抗体)分析结直肠癌组织样本,发现CRY1蛋白水平显著上调,并与肿瘤增殖和患者预后不良相关,提示其作为潜在生物标志物的价值。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of CRY1 Stability and Circadian Function*
**作者**: Saito, T., et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 采用CRY1特异性抗体结合质谱技术,鉴定了CRY1蛋白的磷酸化修饰位点,并证明其通过泛素-蛋白酶体途径调控蛋白稳定性,进而影响昼夜节律周期长度。
---
4. **文献名称**: *CRY1 Modulates Hepatic Lipid Metabolism via PPARα Signaling*
**作者**: Lee, J.H., et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 在小鼠肝脏组织中,通过CRY1抗体的免疫荧光染色和ChIP实验,发现CRY1通过抑制PPARα转录活性调节脂质代谢,揭示了其在代谢性疾病中的潜在作用。
---
以上研究均基于CRY1抗体的实验技术(如免疫沉淀、Western blot、免疫组化等),探讨了CRY1在生物钟、癌症及代谢中的分子机制。
CRY1 (Cryptochrome 1) antibodies are essential tools for studying the role of the CRY1 protein, a key regulator of circadian rhythms in mammals. As a core component of the molecular clock, CRY1 interacts with CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimers to repress their transcriptional activity, thereby maintaining 24-hour oscillations in gene expression. Dysregulation of CRY1 is linked to sleep disorders, metabolic syndromes, and cancer progression.
Structurally, CRY1 contains a photolyase-like domain but lacks DNA repair activity, instead functioning as a transcriptional repressor. Antibodies targeting CRY1 (typically raised in rabbits or mice) enable detection of its expression patterns, post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation), and protein-protein interactions. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and co-immunoprecipitation to investigate circadian regulation mechanisms.
Recent research employs CRY1 antibodies to explore its non-circadian roles, including DNA damage response and glucose homeostasis. Commercial antibodies often distinguish CRY1 from its paralog CRY2 through specific epitope recognition. Validation remains crucial due to potential cross-reactivity and varying performance across experimental conditions. Such reagents continue to advance chronobiology research and therapeutic development targeting circadian-related pathologies.
×