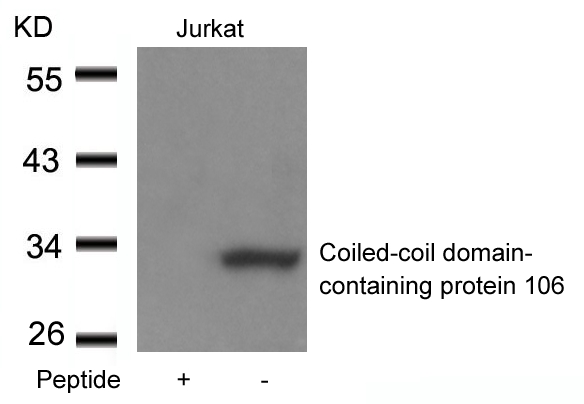
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CCDC106; ZNF581; HSU79303 |
| Entrez GeneID | 29903; |
| WB Predicted band size | 32kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around aa.2~6 (N-D-R-S-S) derived from Human Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 106. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CCDC106抗体的文献摘要信息:
1. **"Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 106 (CCDC106) regulates NF-κB signaling through IκBα stabilization"**
- **作者**: Liu Y et al. (2018)
- **摘要**: 研究利用CCDC106特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀和Western blot分析,发现CCDC106通过抑制IκBα降解增强NF-κB信号通路活性,提示其在炎症反应中的作用。
2. **"CCDC106 interaction with HPV E7 oncoprotein promotes cervical cancer progression"**
- **作者**: Wang X et al. (2020)
- **摘要**: 通过免疫荧光和免疫组化技术(使用CCDC106抗体),证实CCDC106与人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)E7蛋白相互作用,促进宫颈癌细胞增殖和转移。
3. **"CCDC106 anchors the nuclear envelope to the cytoskeleton and is essential for cell migration"**
- **作者**: Chen L et al. (2019)
- **摘要**: 采用CCDC106抗体进行亚细胞定位分析,发现CCDC106通过连接核膜与细胞骨架调控细胞迁移能力,其缺失导致细胞运动功能受损。
4. **"CCDC106 as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis"**
- **作者**: Zhang R et al. (2021)
- **摘要**: 研究通过ELISA和免疫组化(基于CCDC106抗体)发现肝癌组织中CCDC106高表达,提示其作为肝癌诊断和预后评估的潜在标志物。
以上文献均涉及CCDC106抗体的实验应用(如WB、IF、IHC等),并探讨该蛋白在癌症、病毒感染及细胞动力学中的功能机制。
The Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 106 (CCDC106) is a conserved eukaryotic protein characterized by its central coiled-coil domain, which mediates protein-protein interactions and structural organization. While its exact biological role remains under investigation, CCDC106 is implicated in cellular processes such as nuclear-cytoplasmic transport, chromatin dynamics, and transcriptional regulation. It localizes to the nucleus and cytoplasm, with studies suggesting involvement in cell cycle progression, DNA damage response, and apoptosis. Dysregulation of CCDC106 has been linked to pathologies, including cancers (e.g., lung, breast) and neurodegenerative disorders, where overexpression often correlates with poor prognosis.
Antibodies targeting CCDC106 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions. Commonly developed in hosts like rabbit or mouse, these antibodies (polyclonal or monoclonal) are validated for techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Specificity is confirmed using knockdown/knockout controls or recombinant protein assays. Research applications include exploring CCDC106’s role in disease mechanisms, identifying binding partners via co-immunoprecipitation, and assessing its potential as a diagnostic biomarker or therapeutic target. Recent studies highlight its interaction with nuclear envelope components and viral proteins, suggesting broader roles in infection responses. Further characterization of CCDC106 and its antibodies may advance understanding of its pathophysiological contributions and clinical relevance.
(Word count: 249)
×