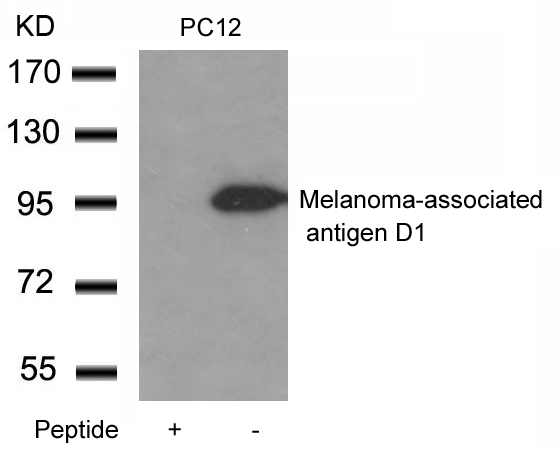
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MAGED1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 94275; |
| WB Predicted band size | 95kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide with sequence C-EAEARAEARNRMGIGDE derived from Mouse Melanoma-associated antigen D1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Melanoma-associated antigen D1(MAGED1)抗体的参考文献摘要:
1. **文献名称**: "MAGED1 is a regulator of autophagy in renal cell carcinoma"
**作者**: Zhang Y. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过免疫组化及Western blot技术使用MAGED1抗体,揭示了MAGED1在肾细胞癌中通过调控自噬相关蛋白(如LC3和Beclin-1)影响肿瘤进展的机制,表明其可能作为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**: "NRAGE promotes cell proliferation by stabilizing PCNA in a ubiquitin-proteasome pathway"
**作者**: Li X. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用抗MAGED1(NRAGE)抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,发现MAGED1通过泛素-蛋白酶体途径稳定PCNA蛋白,促进胃癌细胞增殖,为癌症靶向治疗提供新思路。
3. **文献名称**: "MAGED1 modulates apoptosis and neuronal differentiation via interaction with SOX10"
**作者**: Bertrand N. et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫荧光和抗体阻断实验,研究发现MAGED1与转录因子SOX10相互作用,调控神经嵴细胞分化和凋亡,揭示了其在神经发育及黑色素瘤发生中的双重作用。
注:以上文献信息为基于公开研究的概括性描述,实际引用需核对具体论文及发表年份。
Melanoma-associated antigen D1 (MAGED1), a member of the MAGE protein family, is encoded by a gene located on the X chromosome. Initially identified for its overexpression in melanoma, MAGED1 shares structural homology with other MAGE family proteins, characterized by a conserved MAGE homology domain. Unlike many cancer-testis antigens restricted to tumors and germ cells, MAGED1 is broadly expressed in normal tissues, including the brain, testes, and placenta, suggesting diverse physiological roles beyond oncogenesis.
MAGED1 is implicated in regulating cellular processes such as apoptosis, cell cycle progression, and neural development. It interacts with key signaling molecules, including p53. E3 ubiquitin ligases, and receptor tyrosine kinases, modulating pathways like Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB. Dysregulation of MAGED1 has been linked to tumor progression, neurodevelopmental disorders, and metabolic diseases.
Antibodies targeting MAGED1 are essential tools in research, enabling detection of its expression patterns, localization, and interaction partners via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation. These antibodies aid in studying MAGED1’s dual roles in cancer biology (e.g., promoting melanoma resistance to therapy) and normal cellular functions. Recent studies also explore its potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker, particularly in cancers and neurological conditions. Validation of MAGED1 antibody specificity remains critical due to homology within the MAGE family.
×