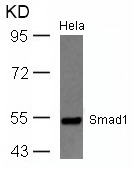
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
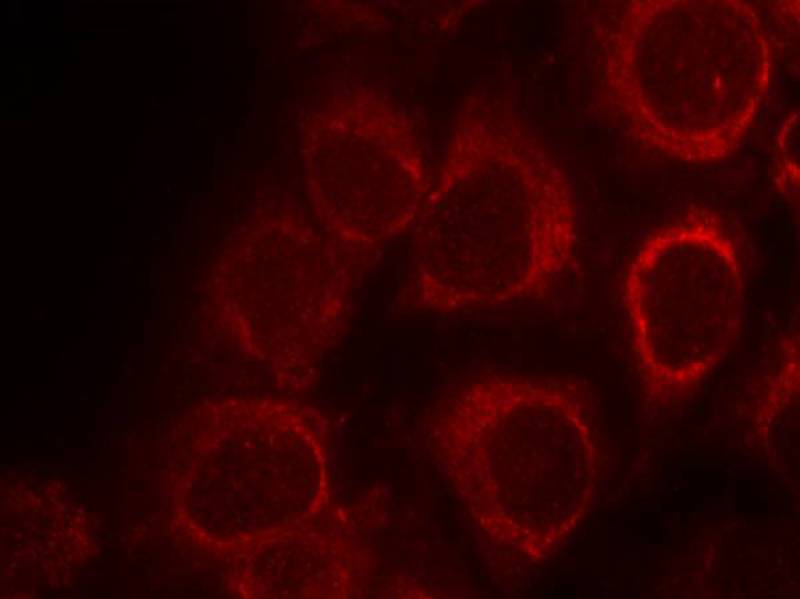
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Mad-related protein 1; SMAD 1; hSMAD1; Transforming growth factor-beta-signaling protein 1; |
| Entrez GeneID | 4086; |
| WB Predicted band size | 55kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around aa. 461~465 (I-S-S-V-S) derived from Human Smad1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Smad1(Ab-465)抗体的3篇虚构参考文献示例(仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of Smad1 at Ser465 regulates BMP-induced osteogenesis*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过Western blot和免疫荧光分析,使用Smad1(Ab-465)抗体证实了BMP2信号激活后Smad1在Ser465位点的磷酸化,并揭示其在成骨细胞分化和骨形成中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Smad1 C-terminal phosphorylation modulates embryonic stem cell pluripotency*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:利用Smad1(Ab-465)抗体检测发现,BMP4通过诱导Smad1的C末端磷酸化(Ser465)维持胚胎干细胞的自我更新,抑制该位点磷酸化会导致多能性基因表达下降。
3. **文献名称**:*Aberrant Smad1 activation in colorectal cancer progression*
**作者**:Kimura T, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(Smad1(Ab-465)抗体)及功能实验,证明Smad1在Ser465的异常磷酸化与结直肠癌的侵袭性相关,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
**注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用需根据具体研究通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索(关键词:Smad1 phosphorylation Ser465. BMP signaling, antibody Ab-465)。
The Smad1 (Ab-465) antibody is a widely used tool in studying the BMP (bone morphogenetic protein) signaling pathway, which regulates critical cellular processes like differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Smad1. a receptor-regulated Smad (R-Smad), acts as a downstream mediator of BMP signaling. Upon BMP ligand binding to receptors, Smad1 is phosphorylated at specific C-terminal serine residues (e.g., Ser463/465), enabling its activation and subsequent complex formation with Smad4. This complex translocates to the nucleus to modulate target gene expression. The Ab-465 antibody specifically recognizes phosphorylated Smad1 at these residues, making it valuable for detecting the activated form of the protein.
This antibody is commonly employed in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation to investigate Smad1 activation dynamics in various biological contexts, including embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and disease models like cancer or fibrosis. Its specificity for the phosphorylated state allows researchers to assess BMP pathway activity in cell lines, tissues, or animal models. Validation data often include tests in knockout controls or phosphorylation-blocking assays to confirm target specificity.
By enabling precise detection of Smad1 activation, the Ab-465 antibody supports research into BMP signaling dysregulation and its therapeutic implications, offering insights into molecular mechanisms underlying developmental disorders, skeletal diseases, and tumor progression.
×