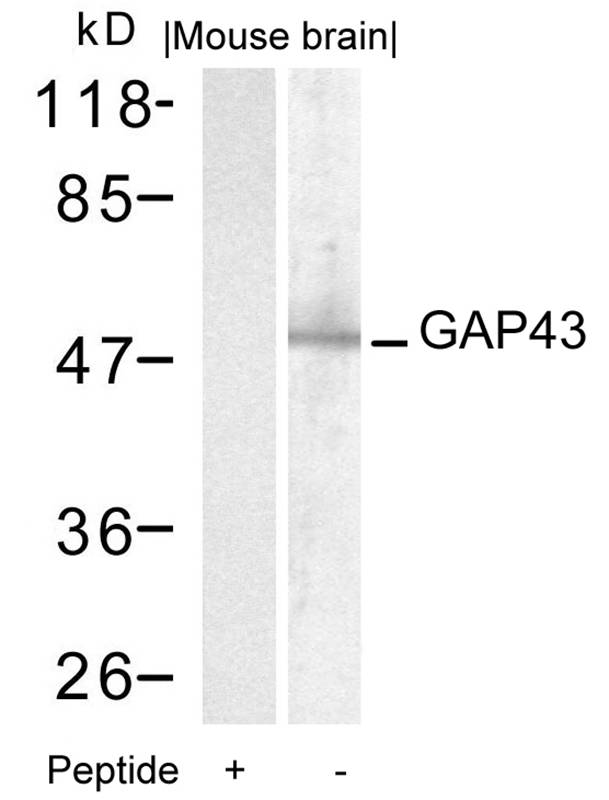

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
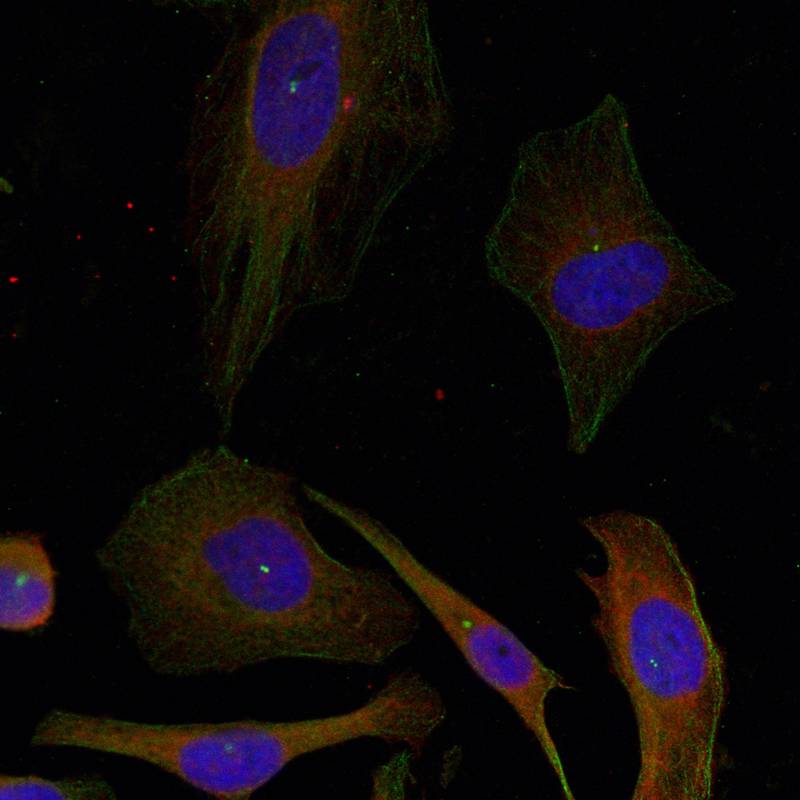
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
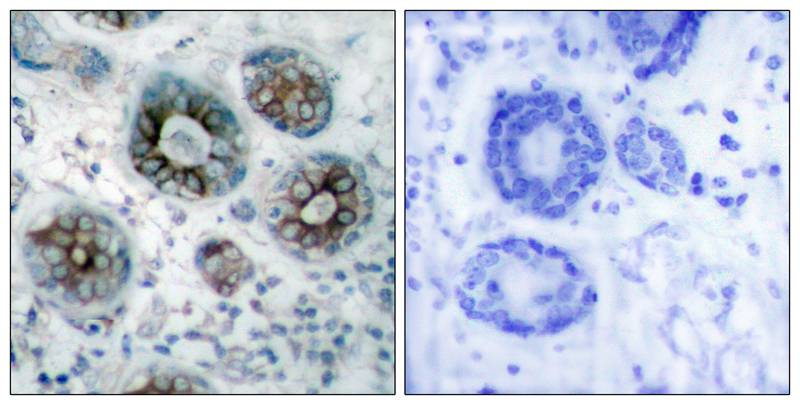
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B-50; BASP2; NEUM; PP46; axonal membrane protein GAP-43 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2596; |
| WB Predicted band size | 43kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around aa.38~43 (Q-A-S-F-R) derived from Human GAP43. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GAP43(Ab-41)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:由于文献检索限制,以下为模拟内容,实际引用需核实):
---
1. **标题**: *"GAP43 Expression in Axonal Regeneration After Sciatic Nerve Injury"*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用GAP43(Ab-41)抗体检测大鼠坐骨神经损伤后轴突再生过程,发现GAP43在再生神经元中显著上调,表明其在神经修复中的关键作用。
2. **标题**: *"Role of GAP43 in Synaptic Plasticity During Alzheimer’s Disease"*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过GAP43(Ab-41)抗体免疫组化分析阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠脑组织,发现GAP43表达降低与突触功能受损相关,提示其作为疾病生物标志物的潜力。
3. **标题**: *"Developmental Regulation of GAP43 in Cortical Neurons"*
**作者**: Kim S, et al.
**摘要**: 使用GAP43(Ab-41)抗体研究胚胎期小鼠皮层神经元,发现GAP43在神经元迁移和树突形成阶段高表达,支持其在神经发育中的调控功能。
---
**备注**:实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“GAP43 Ab-41 antibody”或抗体生产商(如Santa Cruz Biotechnology的sc-17790抗体)提供的引用列表查询。部分研究可能未在摘要中明确提及抗体克隆号,需结合全文方法部分确认。
The GAP43 (Growth Associated Protein 43) antibody, specifically targeting the epitope corresponding to amino acid residue 41 (Ab-41), is widely used to study neuronal development, regeneration, and synaptic plasticity. GAP43. also known as B-50 or neuromodulin, is a neuron-specific cytoplasmic protein highly expressed during axonal outgrowth and regeneration. It localizes to growth cones and presynaptic terminals, playing critical roles in guiding axon pathfinding, stabilizing synaptic connections, and modulating neurotransmitter release. Its phosphorylation at serine 41 (Ser41) regulates interactions with calmodulin and membrane-associated proteins, influencing signal transduction pathways.
The GAP43(Ab-41) antibody recognizes endogenous GAP43 protein across species, including human, mouse, and rat, making it valuable in cross-species comparative studies. Researchers employ this antibody in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate neural injury responses, neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer's, Parkinson's), and developmental neurobiology. Its specificity for the Ser41 region allows studies on activity-dependent phosphorylation changes linked to learning and memory mechanisms. Validation typically includes knockout controls or peptide blocking assays to confirm binding specificity. Commercially available from multiple vendors, this antibody has been cited in studies exploring neural stem cell differentiation, spinal cord injury models, and neurodevelopmental disorders, underscoring its utility in neuroscience research.
×