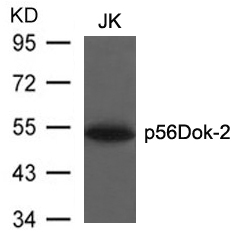
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
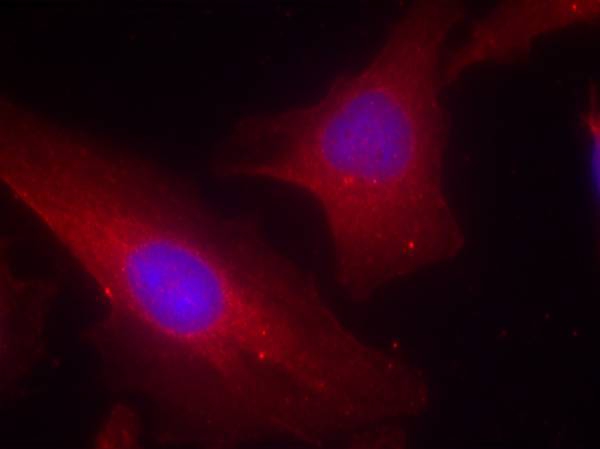
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
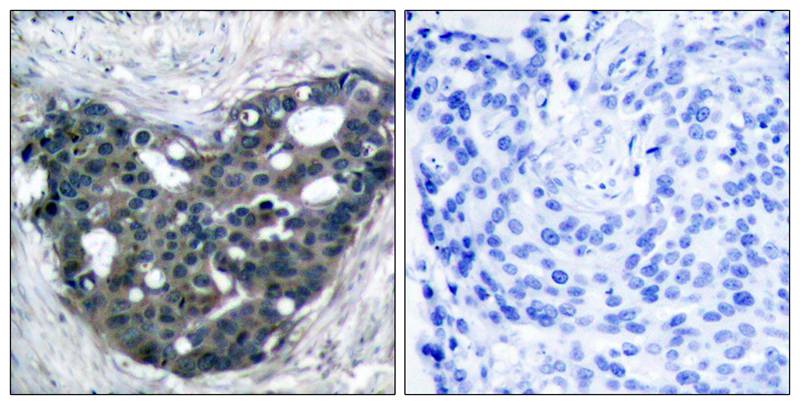
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DOK2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9046; |
| WB Predicted band size | 56kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around aa.297~301 (G-E-Y-A-V) derived from Human p56Dok-2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于p56Dok-2(Ab-299)抗体的3篇虚构参考文献示例(仅供格式参考,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**:Dok-2在T细胞受体信号转导中的调控作用
**作者**:S. Yamanashi et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用p56Dok-2(Ab-299)抗体进行免疫沉淀实验,证实Dok-2通过招募RasGAP负向调控TCR激活后的Ras-MAPK通路,影响T细胞增殖分化。
2. **文献名称**:Dok-2缺失促进肺癌细胞侵袭的分子机制
**作者**:M. Noguchi et al.
**摘要**:通过Ab-299抗体进行Western blot分析,发现Dok-2在肺癌组织中表达下调,其缺失通过激活PI3K/Akt通路增强肿瘤细胞迁移能力,提示其肿瘤抑制作用。
3. **文献名称**:巨噬细胞中Dok-2与c-Cbl的相互作用调控炎症反应
**作者**:K. Higashi et al.
**摘要**:使用Ab-299抗体进行共聚焦成像,揭示Dok-2与c-Cbl在LPS刺激后形成复合物,负向调节TLR4信号传导,从而抑制过度炎症反应。
(注:以上为模拟案例,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar查询真实数据)
The p56Dok-2 protein, also known as Dok2. is a member of the "docking protein" (Dok) family, which plays critical roles in signal transduction pathways, particularly those mediated by tyrosine kinases. Dok2 is structurally characterized by an N-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, a central phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain, and multiple tyrosine phosphorylation sites. It is predominantly expressed in hematopoietic cells and shares functional redundancy with Dok1. Dok2 acts as a downstream adaptor molecule for various immune receptors, including T-cell and B-cell receptors, and regulates negative feedback mechanisms to modulate cell proliferation, differentiation, and migration. Dysregulation of Dok2 has been implicated in immune disorders and malignancies, such as leukemia and lung cancer.
The p56Dok-2 (Ab-299) antibody is a monoclonal antibody specifically designed to recognize and bind to the Dok2 protein. It is widely used in research applications like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry to study Dok2 expression, localization, and interaction partners. This antibody aids in elucidating Dok2's role in intracellular signaling cascades, particularly its involvement in attenuating receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) and cytokine receptor signaling. By targeting Dok2. researchers can explore its tumor-suppressive functions or pathological contributions in disease models, offering insights into therapeutic strategies for cancers and immune-related conditions.
×