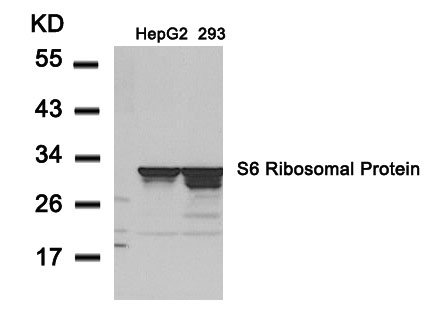
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
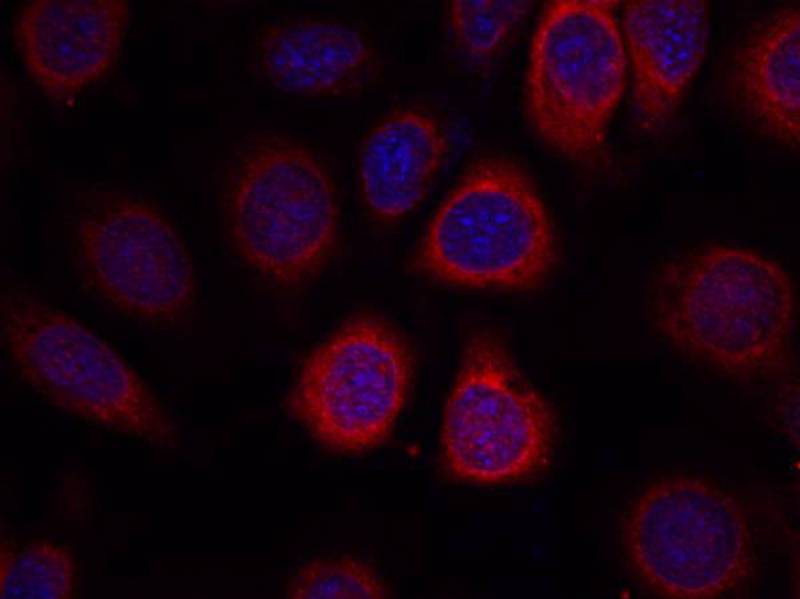
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
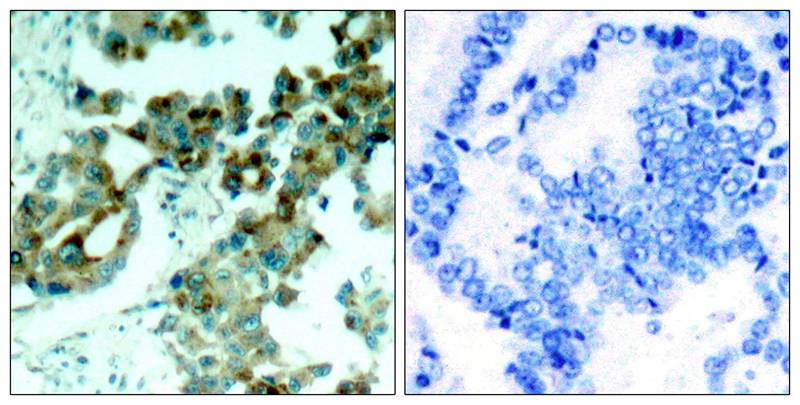
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NP33; RPS6; RS6 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6194; |
| WB Predicted band size | 32kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around aa. 233~237 (R-L-S-S-L) derived from Human S6 Ribosomal Protein. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于S6 Ribosomal Protein (Ab-235)抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
1. **"Phosphorylation of Ribosomal Protein S6 by S6 Kinase and Its Role in Cell Proliferation"**
- **作者**: Volarevic, S., et al.
- **摘要**: 研究了S6蛋白在Ser235/236位点的磷酸化与细胞增殖的关系,发现其通过调控核糖体生物合成影响细胞周期进程,并验证了相关抗体的特异性。
2. **"mTOR Signaling in Growth Control and Disease"**
- **作者**: Laplante, M., & Sabatini, D.M.
- **摘要**: 分析了mTOR通路对S6蛋白磷酸化的调控机制,强调Ser235位点磷酸化在蛋白质翻译和肿瘤发生中的作用,引用了Ab-235抗体的实验数据。
3. **"Ribosomal Protein S6 Phosphorylation in the Nervous System: From Mechanisms to Function"**
- **作者**: Ruvinsky, I., et al.
- **摘要**: 探讨了S6蛋白在神经元中的磷酸化动态,利用Ab-235抗体揭示其在突触可塑性和学习记忆中的功能关联。
这些文献覆盖了S6磷酸化的分子机制、信号通路调控及其在疾病模型中的应用,均涉及Ab-235抗体的实验验证。
The S6 Ribosomal Protein (Ab-235) antibody is a widely used tool in molecular biology for studying the ribosomal protein S6 (RPS6), a component of the 40S ribosomal subunit. RPS6 plays a critical role in regulating protein synthesis, particularly in response to growth factors, nutrient availability, and cellular stress. It is a downstream target of the mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) signaling pathway, where phosphorylation at specific serine residues (e.g., Ser235/236) modulates ribosome biogenesis and translation efficiency. The Ab-235 antibody specifically recognizes RPS6 when phosphorylated at Ser235 (and potentially adjacent residues), making it valuable for monitoring mTORC1 activity and cellular growth states.
This antibody is frequently employed in techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to investigate signaling dynamics in diseases like cancer, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions. Its specificity aids in distinguishing activated pathways under varying physiological or experimental conditions, such as nutrient deprivation or drug treatments targeting mTOR. Researchers also use it to explore tissue-specific regulation of translation and its implications in development, aging, and stress responses. Validation across multiple species (human, mouse, rat) enhances its utility in diverse experimental models.
×