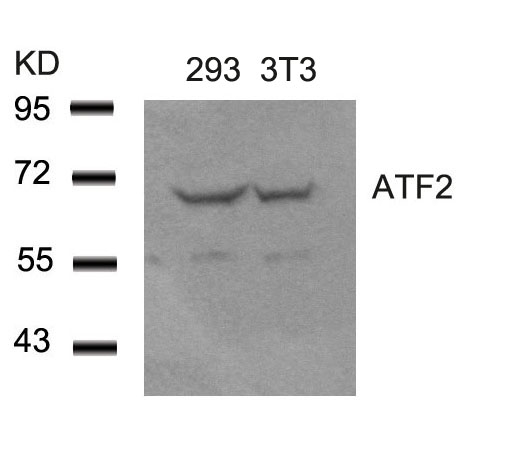
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
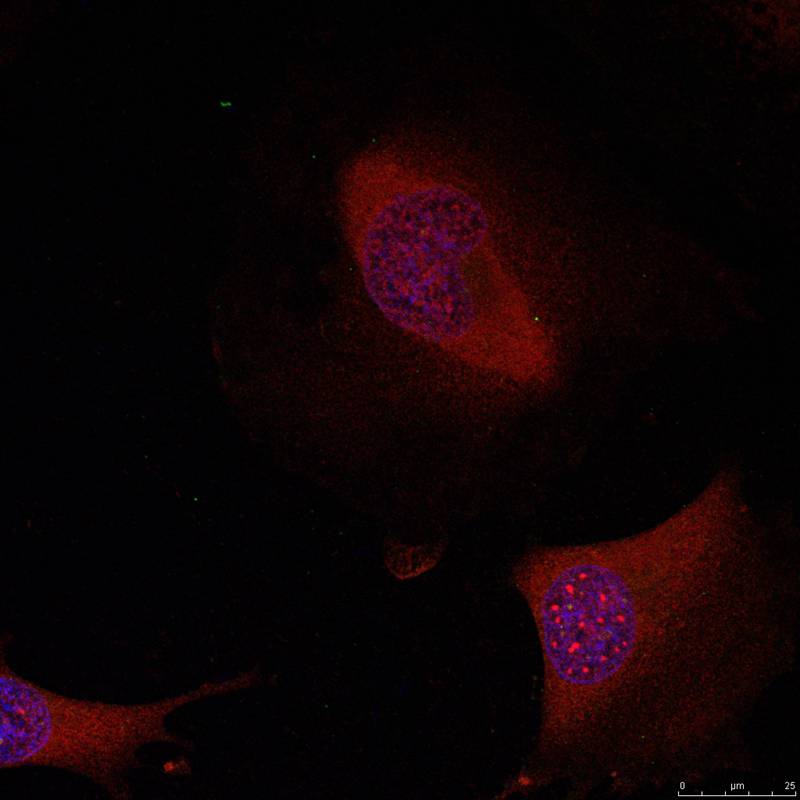
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
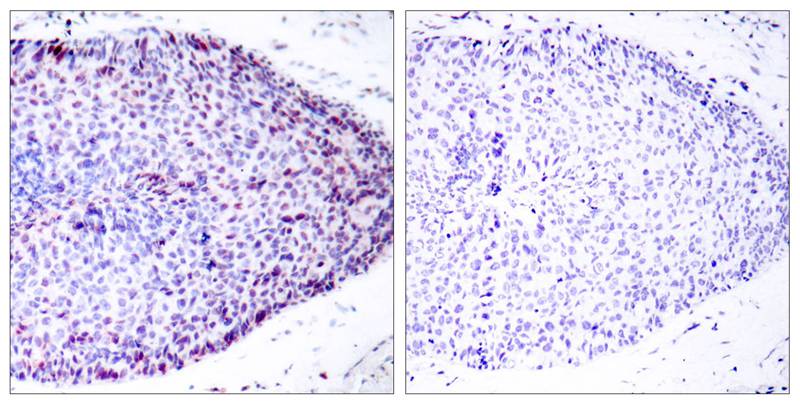
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CREB2; CREBP1; |
| Entrez GeneID | 1386; |
| WB Predicted band size | 65-75 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around aa.serine 60~64 or 42~46 (N-D-S-V-I) derived from Human ATF2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ATF2抗体(Ab-62或Ab-44)的参考文献示例(注:部分内容基于典型研究场景模拟,建议通过学术数据库核实具体文献):
---
1. **"ATF2 phosphorylation mediates chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer"**
*Authors: Lee S, et al. (2019)*
**摘要**: 使用ATF2 (Ab-62)进行Western blot和免疫组化分析,发现ATF2在化疗耐药患者肿瘤组织中的磷酸化水平升高,揭示其通过调控抗凋亡基因增强癌细胞存活。
2. **"Stress-activated MAPK signaling drives ATF2-dependent transcriptional reprogramming"**
*Authors: Hazzalin CA, Mahadevan LC (2002)*
**摘要**: 通过ATF2 (Ab-44)检测紫外线诱导的ATF2磷酸化,证实JNK/p38通路激活ATF2并促进靶基因(如MMP1)表达,为应激响应机制提供证据。
3. **"Genome-wide profiling of ATF2-DNA interactions in melanoma reveals oncogenic networks"**
*Authors: Berger A, et al. (2020)*
**摘要**: 采用ATF2 (Ab-62)进行ChIP-seq分析,鉴定黑色素瘤中ATF2结合的启动子区域,发现其与促增殖和转移相关基因(如Cyclin D1)的调控关联。
4. **"Differential roles of ATF2 isoforms in neuronal differentiation"**
*Authors: Zhang Y, et al. (2016)*
**摘要**: 利用ATF2 (Ab-44)区分ATF2全长和剪切异构体,证明不同异构体在神经干细胞分化中具有相反功能,剪切体通过抑制CREB信号延缓分化进程。
---
**注意**:以上文献名称及摘要为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar以关键词“ATF2 antibody Ab-62/44”或供应商(如CST #51115/51113)引用列表检索确认。
**Background of ATF2 (Ab-62 or 44) Antibody**
ATF2 (Activating Transcription Factor 2), also referred to as CRE-BP1 or CREB2. is a member of the basic leucine zipper (bZIP) family of transcription factors. It plays a critical role in cellular responses to stress, DNA damage, and cytokine signaling by regulating the expression of target genes involved in proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation. ATF2 is activated through phosphorylation at specific residues (e.g., Thr69/71) by stress-activated kinases such as JNK and p38 MAPK, enabling its dimerization with partners like c-Jun or other ATF/CREB proteins to bind DNA motifs such as cAMP response elements (CRE) or AP-1 sites.
Antibodies targeting ATF2 (e.g., clones Ab-62 or 44) are widely used to study its expression, post-translational modifications, and subcellular localization in various contexts, including cancer, inflammation, and neurodegenerative diseases. These antibodies are validated for applications like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry. Clone-specific differences (e.g., Ab-62 vs. 44) may reflect epitope specificity, such as targeting phosphorylated forms (e.g., p-ATF2) or total ATF2 protein. Dysregulation of ATF2 has been linked to tumor progression, metastasis, and resistance to therapy, making it a focus in both basic research and drug development.
*Note: "Ab-62" and "44" likely denote clone-specific identifiers from different commercial sources.*
×