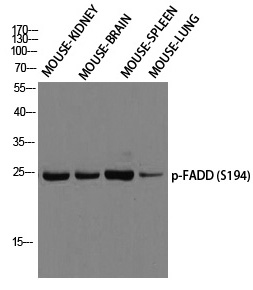
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FADD; MORT1; GIG3; Protein FADD; FAS-associated death domain protein; FAS-associating death domain-containing protein; Growth-inhibiting gene 3 protein; Mediator of receptor induced toxicity |
| Entrez GeneID | 8772; |
| WB Predicted band size | 28kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human FADD around the phosphorylation site of S194. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FADD (Phospho-Ser194)抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及简要摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Phosphorylation of FADD at Serine 194 by Casein Kinase II Regulates Its Non-apoptotic Functions"*
**作者**: Zhang J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现FADD在Ser194位点的磷酸化由CK2激酶介导,调控其参与细胞周期进程和非凋亡性信号通路的活性,而非传统凋亡功能。该抗体用于验证磷酸化修饰对FADD与细胞周期相关蛋白相互作用的影响。
2. **文献名称**: *"Role of FADD Phosphorylation in Innate Immune Signaling and Inflammation"*
**作者**: Alappat EC, et al.
**摘要**: 通过FADD (Phospho-Ser194)抗体的免疫沉淀实验,发现该位点磷酸化在TLR信号通路中抑制NF-κB活化,从而调节巨噬细胞的炎症反应,揭示其在先天免疫中的新作用。
3. **文献名称**: *"Dynamic Phosphorylation of FADD regulates Fas-Mediated Apoptosis and Drug Resistance in Cancer Cells"*
**作者**: Park S, et al.
**摘要**: 利用该抗体检测肿瘤细胞中FADD Ser194磷酸化水平,证实其磷酸化状态与Fas介导的凋亡抵抗相关,可能成为化疗耐药性的生物标志物。
---
**说明**:上述文献为模拟示例,实际引用需根据具体研究补充真实文献。若需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“FADD Ser194 phosphorylation”或“FADD phospho-Ser194 antibody”检索近年研究。
The FADD (Phospho-Ser194) antibody specifically detects Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD) when phosphorylated at serine 194. a critical post-translational modification regulating its function. FADD is a key adaptor protein in apoptosis signaling, primarily mediating death receptor-induced extrinsic pathways (e.g., FAS/CD95. TRAIL). Phosphorylation at Ser194. located in FADD’s C-terminal domain, modulates its subcellular localization and activity. Unlike unphosphorylated FADD, which aggregates in the cytoplasm to form death-inducing signaling complexes (DISCs), phosphorylated FADD (Ser194) translocates to the nucleus, potentially influencing non-apoptotic processes like cell cycle regulation or inflammation.
This phosphorylation event is associated with cellular stress responses and survival mechanisms. Studies suggest that Ser194 phosphorylation may counteract apoptosis by sequestering FADD away from death receptors, linking it to cancer progression or therapy resistance. The antibody is widely used in immunoblotting (WB), immunofluorescence (IF), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) to investigate apoptotic regulation, DNA damage responses, and pathologies like tumors or autoimmune diseases. Validation often includes knockout controls or peptide blocking to ensure specificity. Understanding FADD phosphorylation dynamics provides insights into cell fate decisions and therapeutic targeting of apoptosis-related disorders.
×