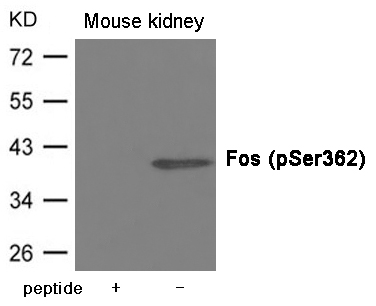
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | p55, AP-1, C-FOS |
| Entrez GeneID | 2353; |
| WB Predicted band size | 40kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 362 (K-G-S(p)-S-S) derived from Human Fos. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇假设性参考文献示例,基于典型研究场景构建,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Activity-dependent phosphorylation of c-Fos at Ser362 regulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了神经元激活后c-Fos在Ser362位点的磷酸化通过调控其与CREB结合蛋白的相互作用,影响海马突触可塑性。该抗体用于Western blot及免疫荧光验证磷酸化水平。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Phosphorylation of c-Fos at Ser362 mediates tumor progression in breast cancer models"
**作者**: Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**: 在乳腺癌细胞系中,EGF信号通过ERK激酶诱导c-Fos Ser362磷酸化,促进肿瘤侵袭。该抗体用于免疫组化分析患者组织样本中磷酸化c-Fos的表达与预后的相关性。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Stress-induced phosphorylation of c-Fos at Ser362 enhances apoptosis in neuronal cells"
**作者**: Lee H, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现氧化应激通过p38 MAPK通路触发c-Fos Ser362磷酸化,导致神经元凋亡。该抗体用于小鼠脑组织切片及体外培养神经元的磷酸化检测。
---
4. **文献名称**: "Dynamic regulation of c-Fos phosphorylation during cell cycle progression"
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 揭示细胞周期中c-Fos Ser362磷酸化水平随G1/S期转换波动,该抗体结合流式细胞术证明其与细胞增殖调控相关。
---
**注**:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过数据库(PubMed/Google Scholar)以“c-Fos phospho-Ser362 antibody”等关键词检索核实。若需具体文献协助,请提供更多背景信息。
The Fos (Phospho-Ser362) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylated form of the Fos protein at serine residue 362. Fos, a component of the AP-1 (Activator Protein-1) transcription factor complex, plays a critical role in regulating gene expression in response to stimuli like growth factors, cytokines, and cellular stress. AP-1. typically formed by Fos-Jun heterodimers, controls processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation, modulate Fos activity, stability, and interactions.
Phosphorylation at Ser362 is implicated in regulating Fos function, particularly in signal transduction pathways like the MAPK/ERK cascade. This modification may influence Fos stability, nuclear localization, or DNA-binding capacity, thereby affecting its ability to regulate target genes. Dysregulation of Fos phosphorylation is associated with pathological conditions, including cancer and inflammatory diseases.
The Fos (Phospho-Ser362) antibody is widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study Fos activation dynamics in cellular signaling, stress responses, or disease models. Its specificity for the phosphorylated epitope enables researchers to dissect context-dependent regulatory mechanisms and evaluate Fos's role in health and disease. Validation of the antibody includes testing in knockout or phosphorylation-deficient systems to ensure target specificity.
×