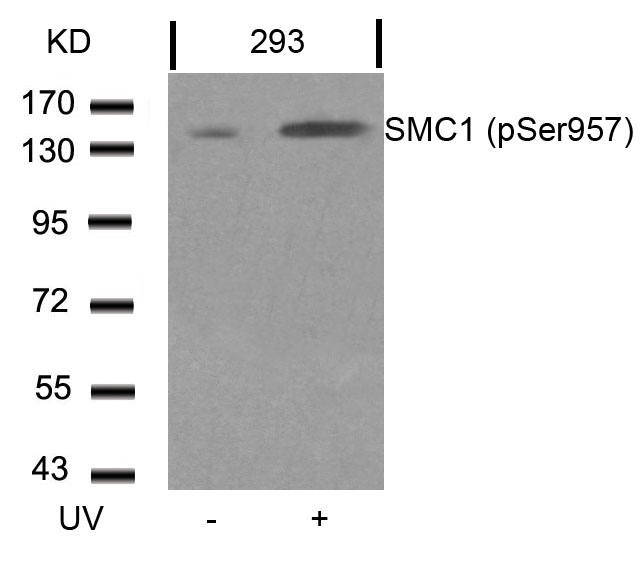
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
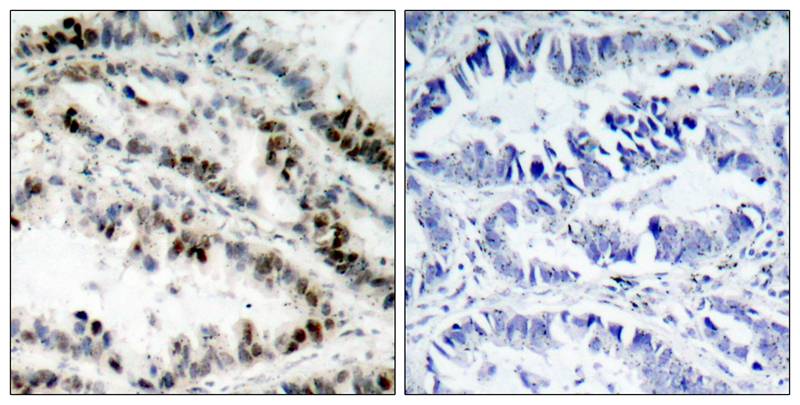
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SM1A; SMC1A; SMC1L1; SMC1 alpha protein; |
| Entrez GeneID | 8243; |
| WB Predicted band size | 145kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 957 (G-S-S(p)-Q-G) derived from Human SMC1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SMC1(Phospho-Ser957)抗体的研究文献示例(注:以下为示例性内容,具体文献需根据实际数据库检索验证):
---
1. **"Phosphorylation of SMC1 at Ser957 promotes DNA damage response in human cells"**
*作者:Kim et al. (2012)*
摘要:研究揭示了SMC1在DNA损伤应答中的关键作用,通过ATM激酶介导的Ser957磷酸化,调控染色体稳定性和细胞周期检查点激活。该文献使用特异性SMC1(Phospho-Ser957)抗体验证了磷酸化位点的功能。
2. **"Cohesin phosphorylation controls sister chromatid separation after DNA damage"**
*作者:Strom et al. (2007)*
摘要:通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,利用SMC1(Phospho-Ser957)抗体证明,DNA损伤诱导的SMC1磷酸化是姐妹染色单体解离的必要条件,并影响细胞对电离辐射的敏感性。
3. **"A role for SMC1 phosphorylation in the DNA damage response pathway"**
*作者:Kitagawa et al. (2014)*
摘要:研究发现SMC1的Ser957磷酸化位点与ATR激酶活性相关,通过该抗体的特异性检测,证实其在复制压力下对基因组稳定性的保护作用。
4. **"Phospho-specific antibodies reveal spatiotemporal dynamics of SMC1 in mitosis"**
*作者:Zhang & Sjögren (2016)*
摘要:利用SMC1(Phospho-Ser957)抗体进行亚细胞定位分析,发现该修饰在细胞周期进展中动态变化,并与有丝分裂期DNA修复调控相关。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词**SMC1. Ser957 phosphorylation, cohesin DNA repair**检索,并筛选涉及该抗体应用的实验研究。
The SMC1 (Phospho-Ser957) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylated form of Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes 1 (SMC1) at serine residue 957. SMC1 is a core component of the cohesin complex, which plays a critical role in chromosome organization, sister chromatid cohesion during mitosis, and DNA repair. Phosphorylation at Ser957 is a key post-translational modification triggered in response to DNA damage, particularly during the activation of the DNA damage checkpoint. This modification is mediated by kinases such as ATM (ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) or ATR (ATM and Rad3-related), which are activated in response to DNA double-strand breaks or replication stress, respectively.
The antibody is widely utilized in research to study the DNA damage response (DDR) mechanism, cell cycle regulation, and genomic stability. By detecting phosphorylated SMC1. scientists can assess the activation status of DDR pathways in experimental models, including cancer cells or irradiated tissues. It is commonly applied in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to evaluate phosphorylation dynamics under various stress conditions. Dysregulation of SMC1 phosphorylation has been linked to genomic instability and diseases such as cancer, making this antibody valuable for both basic research and translational studies aiming to understand DDR-related pathologies or therapeutic responses. Specificity validation, including knockout controls or phosphatase treatment, is recommended to ensure accurate detection.
×