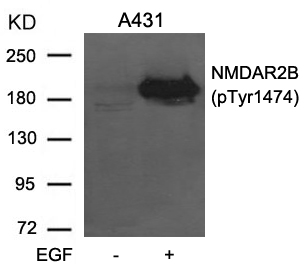
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
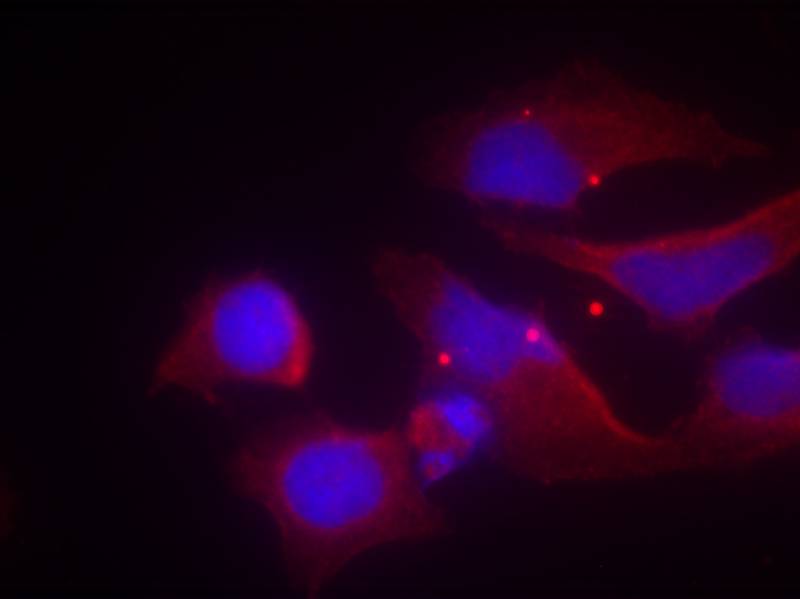
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GRIN2B; NMDE2; NME2; NR2B; NR3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2904; |
| WB Predicted band size | 190kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of Tyr1474 (H-V-Y(p)-E-K) derived from Human NMDAR2B. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NMDAR2B(phospho-Tyr1474)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要信息:
1. **文献名称**:*Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the endocytosis and surface expression of NMDA receptors*
**作者**:Prybylowski K, et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了Tyr1474磷酸化在NMDAR2B亚基内吞中的作用,使用特异性抗体证明其磷酸化状态通过结合AP-2复合物调控受体稳定性,影响突触传递。
2. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of tyrosine 1472 in GluN2B is required for the regulation of NMDAR by Src family kinases*
**作者**:Nakazawa T, et al.
**摘要**:通过phospho-Tyr1474抗体验证,Tyr1472(原文编号可能存在差异)磷酸化是Src激酶调控NMDA受体通道活性的关键,影响神经元兴奋性毒性及缺血性脑损伤。
3. **文献名称**:*Dynamic regulation of NMDA receptor trafficking by tyrosine phosphorylation*
**作者**:Lavezzari G, et al.
**摘要**:该文献利用特异性抗体发现,Tyr1474磷酸化通过阻止网格蛋白介导的内吞作用维持NMDAR2B在突触膜表面的定位,从而调控突触可塑性与学习记忆功能。
(注:Tyr位点编号可能因物种或文献版本差异略有不同,需结合具体实验验证。)
The NMDAR2B (phospho-Tyr1474) antibody is a specialized tool used to study the phosphorylation state of the NR2B subunit (GluN2B) at tyrosine residue 1474 (Y1474) in N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs). NMDARs are ionotropic glutamate receptors critical for synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. The NR2B subunit, a key component of these receptors, regulates channel activity, trafficking, and downstream signaling. Phosphorylation at Y1474. mediated by Src-family kinases like Fyn, modulates receptor internalization and synaptic stability, influencing neuronal excitability and synaptic strength. Dysregulation of this phosphorylation site is implicated in neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, ischemic brain injury, and epilepsy.
The phospho-specific antibody enables detection of Y1474 phosphorylation, serving as a biomarker for studying NMDAR dynamics in physiological and pathological contexts. Researchers employ it in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess phosphorylation levels in cell cultures, animal models, or postmortem brain tissues. Its specificity helps unravel mechanisms underlying synaptic adaptation, excitotoxicity, and therapeutic interventions targeting NMDAR dysfunction. Validation via knockout controls or peptide competition ensures reliability. Understanding Y1474 phosphorylation provides insights into receptor turnover, synaptic remodeling, and disease mechanisms linked to NMDAR hyperactivity or hypoactivity.
×