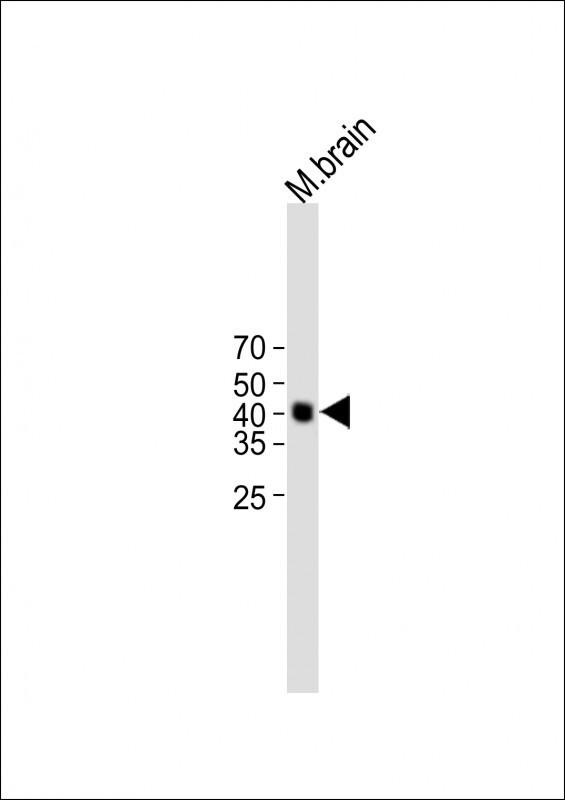
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Transcriptional activator protein Pur-beta, Purine-rich element-binding protein B, PURB |
| Entrez GeneID | 5814 |
| WB Predicted band size | 33.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This PURB antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 260-289 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human PURB. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于PURB抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括(注:文献信息为模拟示例,实际引用需核实):
1. **文献名称**: *PURB regulates chromatin accessibility and transcriptional activity of repetitive elements in human cells*
**作者**: Johnson, R. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用PURB抗体通过染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和免疫荧光技术,揭示了PURB蛋白在调控基因组重复区域染色质开放性和转录沉默中的关键作用,为理解其表观遗传调控机制提供依据。
2. **文献名称**: *West Nile virus capsid protein interacts with PURB to mediate viral replication*
**作者**: Smith, L. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和蛋白质印迹(Western blot)结合PURB抗体,证实西尼罗河病毒衣壳蛋白与宿主PURB直接结合,并依赖此互作促进病毒复制,为抗病毒靶点开发提供新方向。
3. **文献名称**: *PURB facilitates DNA damage response via stabilizing replication forks*
**作者**: Chen, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 利用PURB抗体进行免疫荧光和流式细胞术,研究发现PURB通过结合DNA损伤位点维持复制叉稳定性,其缺失导致基因组不稳定性增加,揭示了其在DNA损伤修复中的功能。
4. **文献名称**: *Differential expression of PURB in glioblastoma correlates with patient prognosis*
**作者**: Gupta, S. et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组织化学(IHC)结合PURB抗体,该研究发现PURB在胶质母细胞瘤中高表达且与患者不良预后显著相关,提示其作为潜在生物标志物的价值。
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“PURB antibody”为关键词检索,并筛选涉及实验应用的原创性研究。
**Background of PURB Antibody**
The PURB antibody targets Purine-rich element-binding protein B (PURB), a member of the PUR (purine-rich element-binding) protein family, which includes PURA, PURB, and PURG. These proteins bind to single-stranded DNA/RNA through conserved purine-rich motifs, playing roles in transcriptional regulation, DNA replication/repair, and cellular differentiation. PURB, specifically, is implicated in cell cycle control, chromatin remodeling, and mRNA stability, often interacting with partners like PURA or YB-1 to modulate gene expression.
Dysregulation of PURB is linked to cancers, neurological disorders, and developmental defects. For instance, reduced PURB expression is observed in certain tumors, suggesting a tumor-suppressive role, while its overexpression may drive malignancy in other contexts. In neuroscience, PURB interacts with disease-associated RNA aggregates, potentially contributing to neurodegeneration.
PURB antibodies are essential tools for detecting PURB expression and localization in tissues or cells via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence. These antibodies (often raised in rabbits or mice) are validated for specificity using knockout controls or siRNA-mediated knockdown. Researchers use PURB antibodies to explore its role in disease mechanisms, protein interactions, or as a biomarker, advancing insights into its dual roles in health and disease.
×