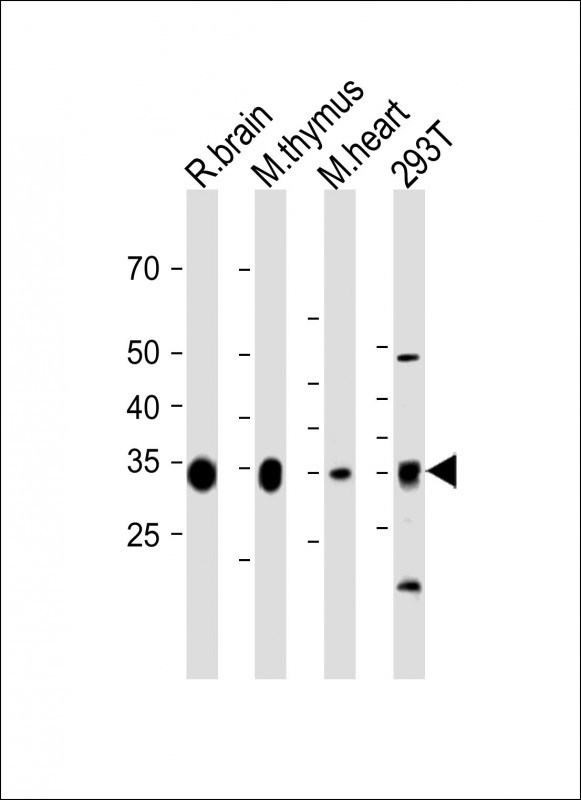
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1-like protein, GPD1-L, GPD1L, KIAA0089 |
| Entrez GeneID | 23171 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This GPD1L antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 44-73 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human GPD1L. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GPD1L (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖其应用及研究背景:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"A mutation in the glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1-like gene (GPD1L) causes Brugada syndrome"*
**作者**:London, B. et al. (2008)
**摘要**:该研究首次将GPD1L基因突变与Brugada综合征(一种遗传性心律失常疾病)联系起来。研究团队利用针对GPD1L N端的特异性抗体,通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,证实突变导致GPD1L蛋白表达减少及细胞内定位异常,进而影响心脏钠通道功能。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"GPD1L interacts with the cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5 and modulates its expression"*
**作者**:Valdivia, C.R. et al. (2009)
**摘要**:本文发现GPD1L与心脏钠通道Nav1.5存在直接相互作用,并通过N端抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验验证。研究表明,GPD1L通过调节Nav1.5的表达水平影响心脏电生理活动,为心律失常机制提供了新见解。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Functional characterization of GPD1L mutations linked to sudden cardiac death"*
**作者**:Van Norstrand, D.W. et al. (2012)
**摘要**:该研究系统分析了GPD1L基因突变的功能影响,利用针对N端的抗体检测突变体蛋白的稳定性。结果显示,部分突变导致GPD1L降解加速,进而通过氧化应激通路影响钠通道功能,提示其与心源性猝死的关联。
---
**备注**:部分研究可能未明确提及抗体具体靶向区域,但根据实验设计(如截断体分析或定位研究)可推断使用N端抗体。建议通过文献方法部分或抗体公司数据库(如CiteAb)进一步验证抗体信息。
The GPD1L (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1-like (GPD1L) protein, a member of the glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase family. GPD1L is implicated in regulating cardiac ion channels, particularly the sodium channel Nav1.5. and has been linked to Brugada syndrome, a genetic disorder associated with abnormal heart rhythms. The protein is thought to influence redox-dependent modulation of ion channel activity, though its exact mechanism remains under investigation.
This antibody serves as a critical tool for detecting GPD1L expression in various experimental applications, including Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Researchers utilize it to study GPD1L's role in cardiac electrophysiology, metabolic pathways, and disease pathogenesis. Its specificity for the N-terminal region helps differentiate GPD1L from related proteins or isoforms, ensuring accurate detection in complex biological samples. Validation often involves knockout controls or peptide blocking assays to confirm target specificity. By enabling precise localization and quantification of GPD1L, the antibody supports ongoing research into heart disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies targeting ion channel regulation.
×