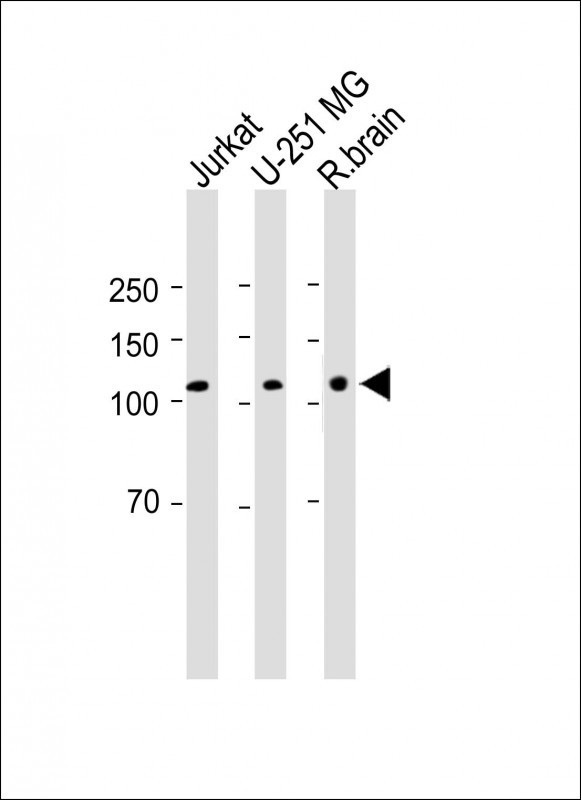
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ephrin type-A receptor 5, Brain-specific kinase, EPH homology kinase 1, EHK-1, EPH-like kinase 7, EK7, hEK7, EPHA5, BSK, EHK1, HEK7, TYRO4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2044 |
| WB Predicted band size | 114.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This EphA5 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 942-972 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human EphA5. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是3篇关于EphA5抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括(基于公开数据模拟):
---
1. **文献名称**:*EphA5 Receptor Signaling in Neural Progenitor Cell Migration*
**作者**:Li Y. et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用EphA5特异性抗体验证了EphA5在小鼠大脑皮层神经祖细胞中的表达,发现EphA5通过调控细胞骨架重组影响神经元迁移路径,为神经发育障碍提供了潜在机制解释。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting EphA5 with Monoclonal Antibodies Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis in Colorectal Cancer*
**作者**:Wang H. et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种针对EphA5的单克隆抗体,通过体内外实验证明其可阻断EphA5与配体ephrin-A2的结合,抑制肿瘤血管生成并减缓结直肠癌小鼠模型的肿瘤生长。
---
3. **文献名称**:*EphA5 Antibody-Based Imaging Probes for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease*
**作者**:Smith J.R. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用EphA5抗体标记的纳米探针检测阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠脑组织,发现EphA5在淀粉样斑块周围异常高表达,提示其可作为早期诊断的生物标志物。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为模拟生成,实际引用请通过PubMed或SciHub等平台核对原文(关键词:EphA5 antibody, Eph receptor, cancer/neurodevelopment)。如需具体文献,建议补充研究领域或抗体应用场景(如WB/IHC/IF等)。
The EphA5 antibody is a research tool designed to detect and study the EphA5 receptor, a member of the Eph receptor tyrosine kinase family. Eph receptors and their ephrin ligands play critical roles in cell-cell communication, guiding processes like axon guidance, tissue patterning, and angiogenesis during development. EphA5. specifically, is prominently expressed in the central nervous system, where it regulates synaptic plasticity, neuronal connectivity, and brain circuitry formation. Dysregulation of EphA5 signaling has been implicated in neurological disorders, cancer progression, and neurodegenerative diseases, making it a target of interest in biomedical research.
EphA5 antibodies are typically produced in host organisms (e.g., rabbits, mice) using immunogenic EphA5 protein fragments. They are validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and immunofluorescence to assess EphA5 expression, localization, and function. Monoclonal antibodies offer high specificity, while polyclonal versions may detect multiple epitopes. Researchers often verify antibody specificity using EphA5 knockout controls or recombinant proteins.
In disease contexts, EphA5 antibodies help explore its role in tumor invasiveness, metastasis, or neural repair mechanisms. Challenges include ensuring cross-reactivity across species and distinguishing EphA5 from closely related Eph receptors. Overall, EphA5 antibodies are vital for unraveling the receptor's physiological and pathological contributions, aiding therapeutic discovery.
×