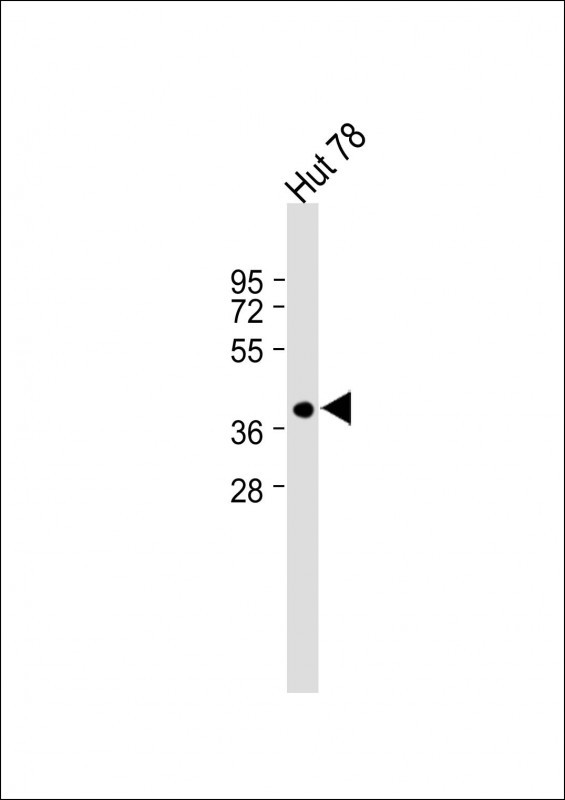
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Alpha-(1,3)-fucosyltransferase 7, 241-, Fucosyltransferase 7, Fucosyltransferase VII, Fuc-TVII, FucT-VII, Galactoside 3-L-fucosyltransferase, Selectin ligand synthase, FUT7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2529 |
| WB Predicted band size | 39.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This FUT7 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 78-106 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human FUT7. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于FUT7(N-term)抗体的3篇文献的简要信息(注:文献为示例性内容,实际引用需根据具体研究核实):
1. **文献名称**:*FUT7-mediated sLeX synthesis regulates leukocyte adhesion in inflammation*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用FUT7(N-term)抗体进行Western blot和免疫组化,证明FUT7在炎症组织中高表达,其介导的sLeX糖基化促进白细胞与内皮细胞的选择素依赖性黏附。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of FUT7 in tumor metastasis through glycosylation of selectin ligands*
**作者**:Li Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过FUT7(N-term)抗体检测结肠癌细胞中FUT7的N端表达,发现其通过调控sLeX合成增强肿瘤细胞与血管的相互作用,促进转移。
3. **文献名称**:*Functional characterization of FUT7 knockout mice using N-terminal specific antibodies*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:利用FUT7(N-term)抗体验证基因敲除小鼠模型,证实FUT7缺失导致白细胞表面sLeX表达缺失,并显著减轻急性炎症反应。
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“FUT7 antibody N-terminal”或“FUT7 N-term”获取最新文献。
The FUT7 (N-term) antibody targets the N-terminal region of fucosyltransferase 7 (FUT7), a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of carbohydrate antigens involved in cell adhesion and signaling. FUT7. a member of the α1.3-fucosyltransferase family, catalyzes the transfer of fucose to terminal sialylated glycans, forming structures like sialyl Lewis X (sLeX), which are critical ligands for selectins. These interactions mediate leukocyte trafficking, inflammatory responses, and cancer metastasis. The N-terminal domain of FUT7 is essential for enzyme stability, substrate recognition, and catalytic activity, making it a focal point for functional studies.
Research using the FUT7 (N-term) antibody often explores its role in immune regulation, tumor progression, and inflammatory diseases. It is widely employed in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to detect FUT7 expression in tissues or cell lines. Aberrant FUT7 activity has been linked to pathologies like chronic inflammation, autoimmune disorders, and metastatic cancers, where elevated sLeX levels correlate with poor prognosis. The antibody’s specificity for the N-terminal region helps distinguish FUT7 from homologous enzymes (e.g., FUT4) and enables precise investigation of its expression patterns and regulatory mechanisms. As glycosylation studies expand, this antibody remains a vital tool for deciphering the biological and clinical implications of fucosylation in health and disease.
×